ABSTRACT
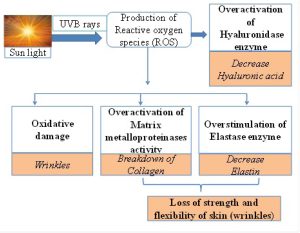
Aging is an inevitable process that results in folds, ridges, and wrinkles in the skin as a result of body mass reduction, insufficient hydration, and breakdown of the connection between the dermis and epidermis. The process of skin aging involves numerous alterations arising from a combination of external factors (such as chemicals, ultraviolet radiation, pollutants, and toxins) and intrinsic factors (such as gene mutation, and hormonal factors). Several pharmacological formulations, such as nanoemulsion, can be used to treat and protect the skin against the damaging effects of reactive oxygen species. Nanoemulsion is a biphasic mixture of two immiscible liquids. Compared to other drug delivery techniques, nanoemulsions can improve drug bioavailability by increasing the absorption rate, reducing variability in absorption, protecting against hydrolysis and oxidation, delivering lipophilic pharmaceuticals and water-soluble drugs. Many drugs may benefit from an aqueous dosage form and increased bioavailability because of the extremely large surface area and low interfacial tension of the whole emulsion system; nanoemulsions have better component penetration ability. Nanoemulsions are also non-toxic and non-irritant and their physical stability can be enhanced. This review article highlights in vitro herbal anti-aging studies on nano emulsions loaded with phytoextracts such as Calendula officinalis, Ocimum basilicum, Coriandrum sativum (coriander), Phyllanthus emblica (Indian Gooseberry), Punica granatum (pomegranate), Tagetes erecta (marigold), Chilli peppers (Capsicum), Oryza sativa (Rice bran), Azadirachta indica (Neem), Daucus carota (Carrot), Camellia sinensis (Green tea), Citrus reticulate (Orange peel) Curcuma longa (turmeric) Morus alba (White mulberry) etc which have anti-aging potential.
