ABSTRACT
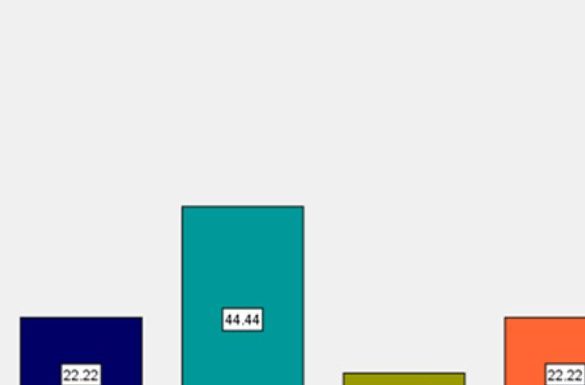
Background: Burning Mouth Syndrome (BMS) is a type of persistent, debilitating orofacial discomfort that is characterized by an oral mucosal burning sensation that does not occur in the presence of any specific oral disease. Aim of this study was to evaluate the clinical features and medication for burning mouth condition. Materials and Methods: We examined the DIAS case file from June 2022 to March 2023, during which 50 samples were identified. Data were gathered using a specific table designed for data collection and a customized examination form. Chi square test and descriptive statistics were used to analyse the data. p>0.05, statistically significant. Results: From the study, around (38.8%) of the participants who had burning mouth syndrome are due to anxiety followed by dryness and irritation (22.2%). Current research shows that around 78% of the participants are female. Majority of the females had anxiety as the main etiological factor compared to males. Pearson chi square-10.68, p>0.016, statistically significant. Majority of the patients used Benzydamine HCl as the topical application (66%) for BMS. Conclusion: Current study proves that, majority of the burning mouth syndrome patients are females and the most common etiological factor has been found to be anxiety. Better management can be provided to patients only when the etiology is understood properly and diagnosed in a right way.
