ABSTRACT
Background
Asthma is a rapidly increasing chronic respiratory disease worldwide. Inhalation drug therapy plays a vital role in asthma management because of immediate pharmacological response. Currently, a wide range of inhaler devices are being used worldwide, among which Metered Dose Inhalers (MDIs) are most commonly prescribed. Adherence with therapy directly depends upon the patient’s satisfaction with inhalation therapy. The current study aimed to determine the asthma patient’s satisfaction with inhalers. As well as the influence of pharmacist led educational intervention upon inhaler satisfaction of asthma patients.
Materials and Methods
The present cross-sectional study recruited 207 physician diagnosed adult asthmatics who were currently using MDI. The patient’s satisfaction with their inhaler was accessed through the study tool- FSI-10 questionnaire. After baseline observations, pharmacist led educational intervention was delivered to asthma patients. The pharmacist personally educated study subjects regarding the proper usage technique and importance of MDIs. Moreover, literature pamphlets containing inhaler technique were provided to patients at the end of intervention. Pre and post intervention satisfaction with inhaler was determined statistically.
Results
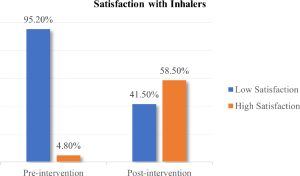
Majority of the asthma patients (197) i.e., 95.2% were observed to have low satisfaction regarding their pressurized meter dose inhalers. Only 4.8% patients presented high satisfaction with inhaler at baseline. However, patients’ satisfaction with their inhalers was raised from 4.8% to 58.5% as the result of intervention. The univariate analysis of the FSI-10 questionnaire data demonstrates a noteworthy association of the intervention given to patients regarding inhaler usage with its effect on the patients’ level of satisfaction with the inhaler. The current study showed p-value of 0.001 (p <0.05) which statistically proves that there is a significant effect of intervention on patients’ level of satisfaction with inhalers.
Conclusion
During baseline survey, majority of the patients presented poor satisfaction with their inhaler. But post intervention evaluation presented an enhancement in patient’s satisfaction with inhalers. Concluding that pharmacist led educational intervention proved to be effective in improving the patient’s satisfaction with inhalers.
