ABSTRACT
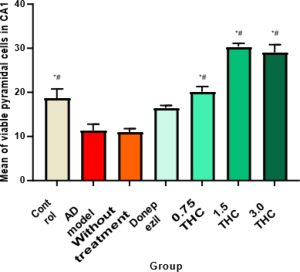
Background: Chronic administration of D-galactose and aluminium chloride (D-gal/AlCl3) has been associated with neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Delta- 9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9THC) is the key psychoactive constituent in Cannabis sativa and has shown promising memory-enhancing capability. This study evaluated the therapeutic effects of Δ9THC on D-gal/AlCl3-induced AD-like rat models through behavioural and histological analysis. Materials and Methods: Healthy male Wistar rats were subjected to AD induction by administering D-gal (60 mg/kg, intraperitoneal injection) and AlCl3 (200 mg/kg, oral) once daily for 10 consecutive weeks. Afterwards, Δ9THC (0.75 mg/kg, 1.5 mg/kg, and 3.0 mg/kg) were administered for 28 days as a treatment phase. Morris Water Maze (MWM) was employed to assess the rats’ behaviour. The structural abnormalities in the hippocampus and neurogenesis markers were assessed. Results: Treatment with Δ9THC alleviated the cognitive dysfunction, as recorded from the MWM, and restored the morphological aberrations in the rat’s hippocampus. Additionally, Δ9THC boosted neurogenesis by marked increased in GFAP+ cells, DCX+ cells, NeuN immunoreactivity and calbindin+ cells. Conclusion: In conclusion, Δ9THC ameliorates D-gal/ AlCl3-induced AD-like cognitive deficits in rat models, which could be linked to its ability to enhance neurogenesis.
