ABSTRACT
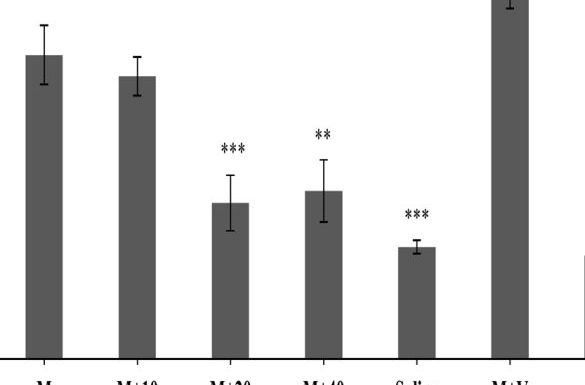
Background: An over-prescription of opioid analgesics triggered the opioid epidemic. Repeated opioid administrations are needed to treat chronic pain, leading to tolerance and physical dependence. Aim: Marrubium vulgare Extract (MVE) was used in this study to investigate its effects on reducing symptoms of Morphine Tolerance (MT) and Withdrawal Syndrome (WS). Materials and Methods: To evaluate MT, 6 rat groups (n=8) were studied in which first group received only morphine (10 mg/kg/day) and the second, third, fourth and fifth ones received morphine with different doses of extract (E20, 40 and80 mg/kg/day) or vehicle (0.25 mL/ rat DMSO) intraperitoneally. The sixth group received only extract (80 mg/kg, i.p as the most effective dose of extract). The hot-plate test was done every other day, 90 min after the injections. In order to study WS, 49 rats were divided into seven groups (n=7), including: morphine, vehicle + morphine, saline, extract (10, 20 and 40 mg/kg) + morphine, and effective dose of extract without morphine (20 mg/kg). Results: The rats were rendered dependent by injection of additive doses of morphine for 9 days. In 9th day, naloxone (4 mg/kg) was injected. Withdrawal signs were calculated for an hour. Complete tolerance was induced in the morphine group on day 7. The groups receiving extract doses of 20, 40, and 80 mg/kg showed complete tolerance on days 9, 11, and 19, respectively. MVE significantly attenuated withdrawal symptoms. Conclusion: At last, the obtained results suggest that M. vulgare extract inhibits morphine tolerance and decreases morphine withdrawal syndrome when co-administered with morphine.
