It is crucial to use a colon-targeted medication delivery system to treat diseases that start in the colon, such as inflammatory bowel disease, colon cancer, amoebiasis, and irritable bowel syndrome. Through colon targeted drug delivery system, we can give localised treatment to the patient which reduces the chance of toxicity and improves its therapeutic efficacy. The bioavailability of medications for the colon has greatly increased because to recent improvements in oral formulations. But because it is intimately linked to GI Inflammation, it is crucial to make some changes to the Gastrointestinal (GI) physiology to increase the therapeutic effect even more. Due to their structural makeup and smaller size, nanoparticles are often used in the administration of drugs that are specifically targeted for the colon. It is designed in such a way that it promotes aggregation time of drugs at the site of action, supporting localized therapy. This review article mainly focuses on oral nanoparticulate formulations that are targeted for treating Colon related diseases.
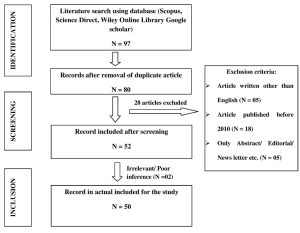
This review aims to explore the prospective scope of excipients obtained from edible natural sources and its unique application in the field of pharmaceutical formulation development. A systematic literature search was conducted using data base like PubMed, Science Direct, Embase, and Google Scholar. A total of 50 articles were identified and reviewed, which primarily focused on the unique application of edible natural sources as excipients in the field of pharmaceutical formulation development. The results revealed that edible natural sources like Dillenia indica, Abelmoschus esculentus; Oryza sativa L; Artocarpus heterophyllus; Tamarindus indica; Musa paradisiaca; Mangifera indica; Ipomoea batatas; Hibiscus sabdariffa and Solanum tuberosum are a promising source of excipients and have great potential to be used in the formulation of pharmaceutical dosage form. Furthermore, the use of these sources may potentially reduce the costs associated with the production of pharmaceuticals dosage form and could also improve the safety profile of the drugs. The review highlights the importance of the use of edible natural sources as excipients and their potential to revolutionize the field of pharmaceutical formulation development.

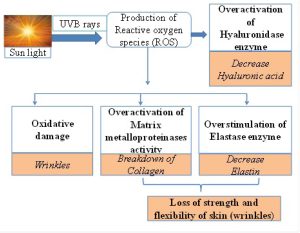
Aging is an inevitable process that results in folds, ridges, and wrinkles in the skin as a result of body mass reduction, insufficient hydration, and breakdown of the connection between the dermis and epidermis. The process of skin aging involves numerous alterations arising from a combination of external factors (such as chemicals, ultraviolet radiation, pollutants, and toxins) and intrinsic factors (such as gene mutation, and hormonal factors). Several pharmacological formulations, such as nanoemulsion, can be used to treat and protect the skin against the damaging effects of reactive oxygen species. Nanoemulsion is a biphasic mixture of two immiscible liquids. Compared to other drug delivery techniques, nanoemulsions can improve drug bioavailability by increasing the absorption rate, reducing variability in absorption, protecting against hydrolysis and oxidation, delivering lipophilic pharmaceuticals and water-soluble drugs. Many drugs may benefit from an aqueous dosage form and increased bioavailability because of the extremely large surface area and low interfacial tension of the whole emulsion system; nanoemulsions have better component penetration ability. Nanoemulsions are also non-toxic and non-irritant and their physical stability can be enhanced. This review article highlights in vitro herbal anti-aging studies on nano emulsions loaded with phytoextracts such as Calendula officinalis, Ocimum basilicum, Coriandrum sativum (coriander), Phyllanthus emblica (Indian Gooseberry), Punica granatum (pomegranate), Tagetes erecta (marigold), Chilli peppers (Capsicum), Oryza sativa (Rice bran), Azadirachta indica (Neem), Daucus carota (Carrot), Camellia sinensis (Green tea), Citrus reticulate (Orange peel) Curcuma longa (turmeric) Morus alba (White mulberry) etc which have anti-aging potential.

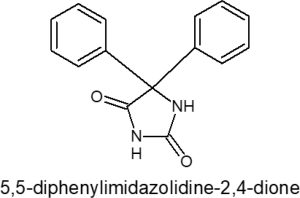
Background: 5, 5-diphenylimidazolidine is a heterocyclic hydrocarbon having unique basic structural characteristics in their molecular structure. In this research; we synthesis various 11 derivatives of -[3-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-oxopropanoyl]- 5,5-diphenylimidazolidine -2,4-dione with anti-fungal activity. The agar well diffusion method was used to conduct the pharmacological screening for antifungal activity. Materials and Methods: All 5, 5-diphenylimidazolidine derivatives were synthesized by conventional method. Benzoin; Benzil; Urea; Glacial Acetic Acid; 4- hydroxyl benzoic acid; Con. HNO3; Formic Acid; 2- Nitro Aniline are used for the synthesis. The structure confirmations were done by FTIR, NMR spectroscopy and MS. Results: In this research; we concluded that; many derivatives give potent anti-fungal activity against fungi. The compound 1-[3-(oxo (phenyl amino)acetic acid)-3-oxopropanoyl]-5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione (BJ); 1-[3-(N-phenylformamide)-3-oxopropanoyl]-5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione (BG); 1-[3-(NPhenyl- 2-nitroaniline)-3-oxopropanoyl]-5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione (BE); shown better antifungal activity against Candida albicans. BJ was shown to be the most effective chemical when compared to Griseofulvin and other common medications because it demonstrated greater antifungal action against Aspergillus niger. Conclusion: The anti-fungal activity of the title compounds and their derivatives was studied. Studies on the link between structure and activity revealed that compounds containing 5, 5-dimethylimidazolidinone derivatives with an electron-withdrawing group have higher activity than those containing an electron-donating group. 1-[3-(N-Phenyl-2-nitroaniline)-3-oxopropanoyl]-5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione (BE); 1-[3-(oxo(phenyl-amino) acetic acid)-3-oxopropanoyl]-5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione (BK) shown better antifungal activity against Candida albicans.
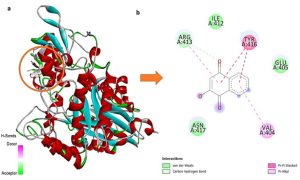
Background: Our previous research highlighted remarkable hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic potentials of lawsone methyl ether (LME or 2-methoxy-1,4-naphthoquinone) and lawsone (2-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone) in diabetic rats via β-cell regeneration. This insighted us to explore their additional antidiabetic mechanisms against α-glucosidase using in silico and in vitro approaches. Materials and Methods: In silico molecular docking was performed via Autodock Vina, SwissADME, and Datawarrior software. However, an in vitro inhibitory assay was conducted against α-glucosidase. Results: In silico studies revealed promising binding conformations and interactions of LME and lawsone with the functional residues of the α-glucosidase protein, involving hydrogen bonding, Van der Waals, and pi-pi interactions, showing comparable binding energies of -5.4 and -5.6 kcal/mol, respectively. Additionally, LME and lawsone displayed favorable pharmacokinetic profiles, revealing no evident toxicity. In vitro α-glucosidase inhibitory assay indicated that LME (IC50 of 37.4 μg/mL) and lawsone (IC50 of 42.2 μg/mL) exhibited comparable inhibitory activities, while both of them possessed markedly higher activities than acarbose (IC50 of 440.6 μg/mL). Furthermore, study on synergistic effects among these naphthoquinones and acarbose illustrated that at ½IC50 of LME (18.7 μg/mL) and acarbose (220.3 μg/mL) exhibited a satisfactory synergistic effect against α-glucosidase, with a percentage inhibition of 88.7% and a fractional percentage inhibition index (FPI) of 2.0, while at ½IC50 of lawsone (21.1 μg/mL) and acarbose (220.3 μg/mL) produced an additive effect, with a percentage inhibition of 76.4% and a FPI of 1.7. Conclusion: Promising α-glucosidase inhibitory potentials of LME and lawsone underscore their additional mechanism alongside β-cell regeneration further supporting their outstanding antidiabetic capabilities.

Background: Momordica charantia (MC), Nigella sativa (NS), and Anethum graveolens (AG) are widely utilized vegetables and as an herbal medicines, despite widespread use, there is no evidence of molecular mechanisms of compound-protein-pathway interaction for the treatment of metabolic syndrome (MetS). Materials and Methods: Reported phytochemicals were collated from the botanical databases and SwissTargetPrediction was utilized to predict likely protein targets. Both the STRING and KEGG databases were used to infer the protein target pathway analysis. Cytoscape v3.6.1 was employed to build the compound-protein-pathway network. AutoDock vina executed through POAP pipeline was employed for therapeutic target and compounds docking study. Molecular dynamics was performed by GROMACS. Results: 34, 19, 34 phytocompounds from three plants MC, NS, and AG were predicted to target 30, 30, 28 protein targets and these targets modulated 20, 18, 22 molecular pathways respectively involved in metabolic syndrome. Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction, Calcium, cGMP-PKG, cAMP, AMPK, PI3K-Akt, PPAR, Metabolic signaling pathways, etc were modulated by compounds. PPARG was hub gene within the network. Nigellidine from NS, Nigellimine-N-Oxide from NS, Cryptoxanthin from MC scored lowest BE with PPARG (-7.5kcal/mol), FABP1 (-8.8kcal/mol), and HMGCR (-7.1kcal/mol) protein targets respectively. MD simulation for 100ns revealed stable interactions of phytocompounds comparable to standard molecules. Conclusion: The current study identified multi-compounds containing enhanced fraction of MC, NS, and AG could be the effective therapy regimen for diabetes, obesity, and MetS.
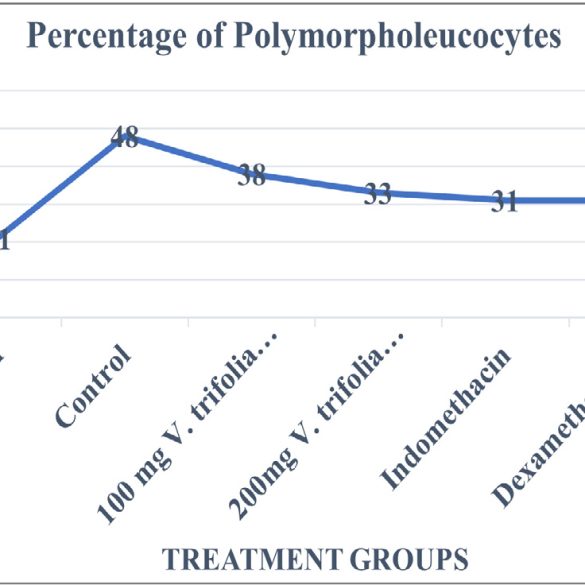
Background: The experiment was intended to evaluate the effect of Vitex trifolia Linn’s hydroalcoholic extract to treat chronic inflammation. Materials and Methods: Chronic inflammation was induced by injecting 0.25 mL of Complete Freund’s Adjuvant subcutaneously in the palmar surface of the right-hand paw of Wistar rats. The animals were treated with two different doses of the plant extract and their efficiency and efficacy was compared to standard drugs indomethacin and dexamethasone for 28days. At the end of the study the serum TNF-α and IL-10 using ELISA kits, differential leukocyte count was estimate, vital organs were subjected to histological studies. The anti-tubercular activity of the extracts of V. trifolia was also evaluated by the Microplate Alamar Blue Assay method (MABA) against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Results: The extract has also been shown to be effective in controlling levels of chemical cytokines IL-10 and TNF-α and the anti-TB activity was evaluated using Alamar Blue Assay which also exhibited promising results. Conclusion: The obtained results implicate that hydroalcoholic extracts of V. trifolia show promising anti-inflammatory action on chronic stage of inflammation and as well as have proven to be effective as anti-tubercular drug.
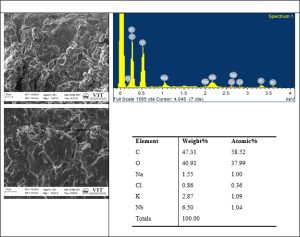
Background: Santha Chandrodaya Mathirai (SSM) [Cāntacantirōtaya māttirai] is a classical tablet formulation in Siddha medicine used in various types of fevers. Because of limited research validation in terms of the product compactness, quality and safety, the present study focuses on the formulation, characterization and standardization of the tablet dosage. The objective of the study is to prepare SSM as per Standard operating Procedures (SoPs) mentioned in classical text and to characterize it chemically using modern analytical techniques. Materials and Methods: The tablet dosage was prepared from the In-house R&D GMP Pharmacy facility of Siddha central research Institute and validated through analytical measures like pre-compression, post-compression parameters, physiochemical analysis, analytical studies like High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography (HPTLC), Special Edition Microscopy (SEM) with Energy Dispersive X-Ray (EDAX), Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) and UV Absorption Spectroscopy (UV-AS). Results: As per the reference standards, the mean flow property of the Tablet granules (31˚) was fair enough, the mean compressibility index (17.3%) and Hausner’s ratio (1.452) indicates its good flow character. The tablet passed the USP standards of weight variation in %. The friability test reported the maximum weight loss to be 0.06 %, a good acceptable value. The highest disintegration time was observed at 60 min. The samples were devoid of Heavy metals, microbial and aflatoxin contamination. At short UV of 254 nm, long UV of 366 nm, and post derivatized plate in white light there were observation of 6 spots, 8 spots and 12 spots respectively in TLC photo documentation. EDAX reported the presence of Carbon, Oxygen, Sodium, Chlorine, Potassium, and Niobium molecules in the sample with no traces of heavy metals. FTIR spectra showed three high peak areas at the range of band 2917.08, 2849.10, and at 1717.08 that corresponds to carboxylic acid, alkane bond, and α, β-unsaturated ester. Conclusion: The In-house samples of SSM reported standard values in terms of quality and safety. Further clinical trials are warranted to validate its efficacy.
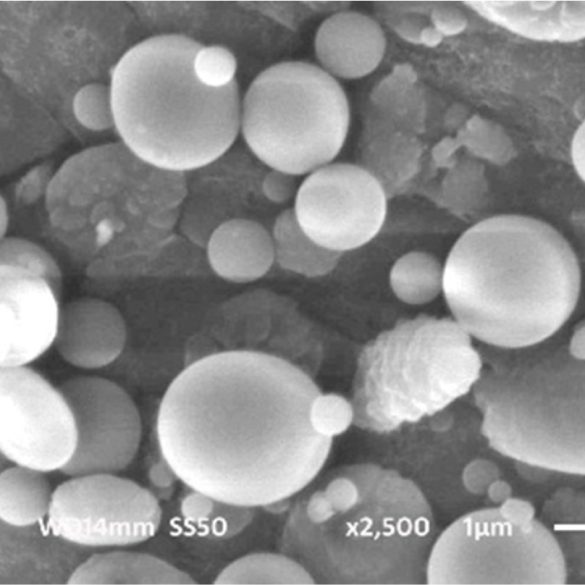


Background: Favipiravir has a low bioavailability, a fast elimination molecule, and severe gastrointestinal side effects. The bioavailability followed by therapeutic efficacy could be improving by sustained release formulation such as nanoparticle. The anti-viral drug favipiravir is made of nanoparticle matrixes through solvent evaporation. Materials and Methods: In this study, the Box-Behnken design with three factors and three levels was heavily utilised to optimise parameters like concentration of polymer (A), sonication frequency (B), and time of sonication (C). Particle size, practical yield, and entrapment effectiveness were three dependent variables that were measured as responses. The independent as well as dependent variables were related using mathematical equations and response surface plots. Results: The designed model formula has a particle size of 343.14 nm, entrapment efficiency of 83.74 percent, and a practical yield of 85.39 percent with respective A, B, and C levels of 750, 37.5, and 40. The results of the observed responses were very similar to those expected by the process that had been optimised. Morphological analysis, and In vitro release study was used to characterise the prepared nanoparticle. Until 24 hr later, the prepared nanoparticle demonstrated good sustained drug release. Conclusion: The factorial design allows large-scale favipiravir nanoparticle synthesis with homogeneous particle size distribution, excellent entrapment efficiency, and practical yield.
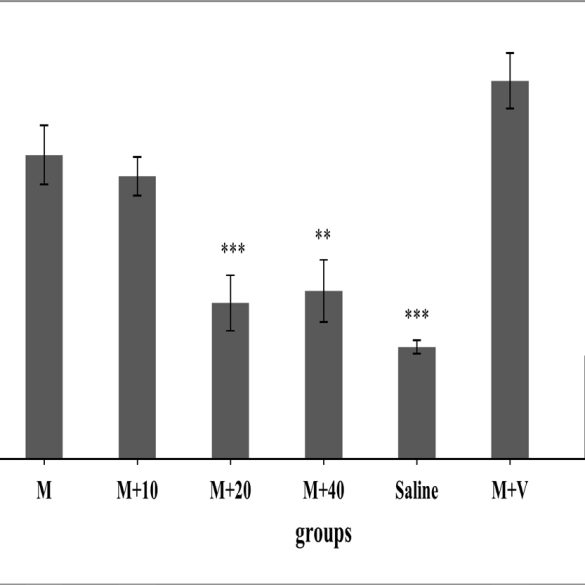
Background: An over-prescription of opioid analgesics triggered the opioid epidemic. Repeated opioid administrations are needed to treat chronic pain, leading to tolerance and physical dependence. Aim: Marrubium vulgare Extract (MVE) was used in this study to investigate its effects on reducing symptoms of Morphine Tolerance (MT) and Withdrawal Syndrome (WS). Materials and Methods: To evaluate MT, 6 rat groups (n=8) were studied in which first group received only morphine (10 mg/kg/day) and the second, third, fourth and fifth ones received morphine with different doses of extract (E20, 40 and80 mg/kg/day) or vehicle (0.25 mL/ rat DMSO) intraperitoneally. The sixth group received only extract (80 mg/kg, i.p as the most effective dose of extract). The hot-plate test was done every other day, 90 min after the injections. In order to study WS, 49 rats were divided into seven groups (n=7), including: morphine, vehicle + morphine, saline, extract (10, 20 and 40 mg/kg) + morphine, and effective dose of extract without morphine (20 mg/kg). Results: The rats were rendered dependent by injection of additive doses of morphine for 9 days. In 9th day, naloxone (4 mg/kg) was injected. Withdrawal signs were calculated for an hour. Complete tolerance was induced in the morphine group on day 7. The groups receiving extract doses of 20, 40, and 80 mg/kg showed complete tolerance on days 9, 11, and 19, respectively. MVE significantly attenuated withdrawal symptoms. Conclusion: At last, the obtained results suggest that M. vulgare extract inhibits morphine tolerance and decreases morphine withdrawal syndrome when co-administered with morphine.
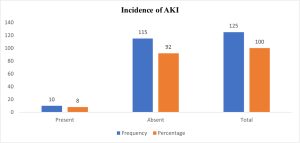
Background: Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) is a common condition and can happen due to drugs like Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) and which can be reversible by discontinuing NSAIDs. This research aims to examine the risk factors and occurrence of AKI in individuals using NSAIDs, while also investigating the potential correlations between AKI and conditions such as hypertension, gout, and emergency medical situations. Materials and Methods: A comprehensive total of 125 patients were included based on specific criteria, encompassing both inclusion and exclusion parameters. The medical histories of these patients were meticulously reviewed, with relevant data duly documented, and concludingly subjected to statistical examination. Results: Among the 125 patients studied, 10 individuals were diagnosed with AKI, resulting in an incidence rate of 8%. Notably, 80% of these AKI cases were observed in the older age group (45-65 years), with 60% being male and 40% female, indicating a higher risk in male patients. Additionally, 40% of the AKI patients had a pre-existing condition of hypertension, which posed a higher susceptibility to AKI development. The diagnosis of AKI was based on laboratory parameter changes, particularly serum creatinine levels, and adhered to the KDIGO scale (Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes). Conclusion: Following the examination of NSAID users, it was concluded that the elderly population and individuals with a history of hypertension face the highest risk of developing AKI, leading to elevated serum creatinine levels. Additionally, male patients exhibited a higher frequency of AKI compared to their female counterparts. Notably, a significant number of patients were found to have taken Diclofenac for an extended duration, which correlated with increased serum creatinine levels and a potential link to AKI development. Consequently, Diclofenac usage warrants consideration as a drug that may contribute to the onset of AKI.

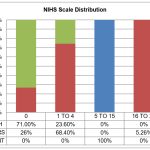
Background: The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved remdesivir under emergency use authorization for the management of the early stage of Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19). Since remdesivir has been approved on a ‘fast-track’ basis, the real-life efficacy and its safety on different population subsets have not been studied in detail so far. This study aimed to investigate the real-life efficacy with a special focus on the cardiovascular safety of remdesivir in the management of COVID-19. Materials and Methods: This is a single-centered, case-control study conducted from April 2022 to March 2023 in 427 case records and 301 records (181 under remdesivir and 120 in the control group) were analyzed. Results: In the severe COVID-19 category, the remdesivir group has significant AST, ALT, blood urea, and serum creatinine elevation when compared to the baseline values. Remdesivir is associated with a significant increase in the occurrence of QT prolongation during therapy (Odds ratio [QT]=3.18 (95% Confidence Interval [CI] 1.13 to 8.93; p=0.038). The Remdesivir group does not differ significantly in all-cause mortality in COVID-19 when compared with that of the control group (35.4% Vs. 33.3%; p=0.804). Conclusion: The use of remdesivir in COVID-19 patients did not reduce all-cause mortality and it is not associated with protective mortality outcomes. Remdesivir causes increased incidence of QT prolongation, bradycardia, and elevation of AST, ALT, Blood urea, and serum creatinine levels in COVID-19 patients.
Background: Dental caries are highly prevalent and if left untreated, it can lead to harmful consequences. Micro-invasive types of dental caries treatment were adopted to cease the progression of decay. Fissure sealant helps to arrest incipient caries in pits and fissures. However, the major concern with conventional pit and fissure sealants is their technique sensitivity due to moisture contamination. Hence, hydrophilic sealants were introduced to overcome this drawback. The objective of the study is to compare and evaluate the micro hardness of conventional and hydrophilic pit and fissure sealants. Materials and Methods: Thirty sound molar teeth were grouped into 2 groups for which 15 molars were assigned to each group. Group I was allocated for 3M ESPE Clinpro hydrophobic sealants and Group II was Ultra-seal XT Hydro hydrophilic sealant. The prepared specimens were acid-etched with 37% phosphoric acid, followed by rinsing with water and finally air-dried before sealant placement. Each sealant material was then applied and light-cured. Vickers hardness test was used to estimate the microhardness of the sample with 200 gm load for 20 sec. Mann Whitney U test was done to find the difference between the two groups and the Wilcoxon test was used to find the difference within the group. Results: The differences between the mean microhardness value and Immediate, Aging time factor were found to be statistically non-significant. An increase in mean value was observed after ageing in both groups. A statistically significant difference (p<0.05) was observed within each group for the immediate and aging time factor. However, the mean microhardness aging value of Group II (30.04±5.31) was comparatively higher than Group I (28.01±4.02). Conclusion: There were no significant differences in the mean values of Group I and Group II for the immediate and aging time factor, but the aging time factor increased the mean values of both groups, and the difference was found to be statistically significant for both the groups. However, Hydrophilic pit and fissure sealants (Group II) had higher aging microhardness mean values compared to conventional sealants (Group I).
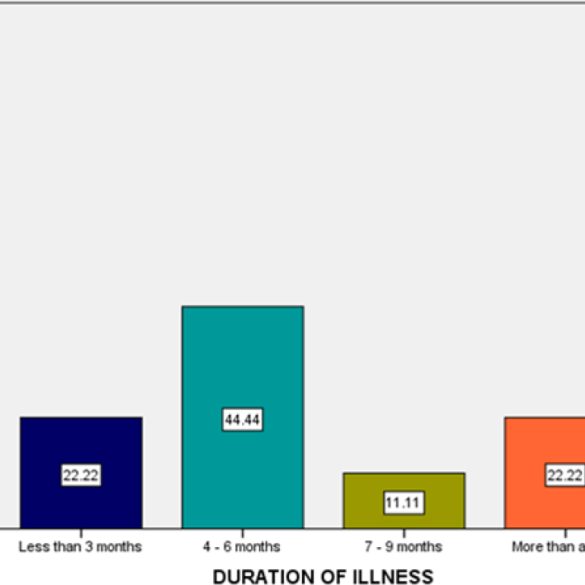
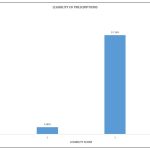
Background: Burning Mouth Syndrome (BMS) is a type of persistent, debilitating orofacial discomfort that is characterized by an oral mucosal burning sensation that does not occur in the presence of any specific oral disease. Aim of this study was to evaluate the clinical features and medication for burning mouth condition. Materials and Methods: We examined the DIAS case file from June 2022 to March 2023, during which 50 samples were identified. Data were gathered using a specific table designed for data collection and a customized examination form. Chi square test and descriptive statistics were used to analyse the data. p>0.05, statistically significant. Results: From the study, around (38.8%) of the participants who had burning mouth syndrome are due to anxiety followed by dryness and irritation (22.2%). Current research shows that around 78% of the participants are female. Majority of the females had anxiety as the main etiological factor compared to males. Pearson chi square-10.68, p>0.016, statistically significant. Majority of the patients used Benzydamine HCl as the topical application (66%) for BMS. Conclusion: Current study proves that, majority of the burning mouth syndrome patients are females and the most common etiological factor has been found to be anxiety. Better management can be provided to patients only when the etiology is understood properly and diagnosed in a right way.

Background: Research studies on drug utilization in inpatient settings serve as valuable tools for assessing drug prescribing trends, efficiency, and the cost-effectiveness of hospital formularies. Our current study focuses on evaluating drug usage patterns, conducting drug audits, and assessing clinical outcomes using WHO indicators in healthcare facilities within tertiary care hospitals. Materials and Methods: In a prospective study conducted at a tertiary care hospital in Tamil Nadu, data were systematically gathered from 800 prescriptions spanning from November 2021 to April 2023. The WHO data collection tool was employed to evaluate prescribing indicators. Patients who either passed away or requested discharge against medical advice within the first 24 hr of admission were excluded from the dataset. The data analysis was carried out using Graph Pad Prism version 10. Results: The average number of drugs per encounter was 2.14. Antibiotics were prescribed in 71% of encounters, while injections were administered in 52%. A total of 80% of drugs were prescribed using generic names in the tertiary care hospital. Regarding hospital stays, 27% of individuals were admitted within three days of treatment, and individuals aged 21 to 40 accounted for more than 35% of the total hospital stays. Conclusion: The study demonstrated that cefotaxime was the most frequently prescribed antibiotic. The average number of drugs in this study was slightly over WHO standards. This research motivates clinicians to increase the use of generic drugs, may reduce the expenditures in health care without affecting the efficacy of the drug, and guide more clinicians towards prescribing generic drugs. However, injectable drugs are more prescribed when compared to other formulations. Further, we recommend studies that need more sample sizes and multicentre studies to estimate the overall prescribing practices of orthopedic ward.

Background: Community pharmacists have an important role in dispensing topical corticosteroids only with prescription. They should be aware about the uses and the potential side effects associated with misuse of topical corticosteroids. It is necessary to educate the community pharmacist regarding the clinical aspects of the topical corticosteroids. Therefore, our study aims to assess, evaluate the Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice (KAP) among Community Pharmacist regarding dispensing of topical corticosteroids and educating community pharmacists. Materials and Methods: A Prospective Pre-Post study carried out among Community Pharmacist. A Self-prepared and validated KAP questionnaires were distributed to the community Pharmacist through face-to-face interview were done after seminar was conducted using audio-video visuals is given then post study was done after 1 month with the same set of questionnaires. Results: Out of 116 Community Pharmacist men made up 80.17% more participants than women. The percentage of people aged 20 to 30 was 33.62%. Most of the participants were diploma holders (Diploma in Pharmacy) with 76.72%. The participants in our study are experienced around 24.14% were having more than 21 years of experience. Pre-test knowledge, attitude, and practice among the pharmacists was less with mean ± standard deviation (46.7±10.33), (65±8.38), (59.83±14.45) compared with post-test knowledge, attitude, and practice was high with mean (87.74±11.03), (87.79±6.56), (82.50±9.50). Post-test showed significant improvement in Knowledge Attitude and Practice score respectively compared to pre-test (p<0.05). Conclusion: Educating community pharmacists regarding topical corticosteroids reduces the misuse of topical corticosteroids by increasing knowledge about topical corticosteroids.

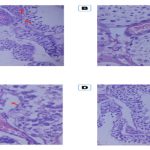
Gingival recession, particularly in the anterior teeth, can lead to functional and aesthetic concerns. It can cause aesthetic deterioration, dentin hypersensitivity, and difficulties in maintaining proper oral hygiene. Multiple surgical methods have been utilized to treat gingival recession. This article presents a case where the lateral pedicle technique combined with a Subepithelial Connective Tissue Graft (SCTG) was successfully utilized to cover the exposed root surface of a single tooth. The adjacent soft tissue was repositioned over the recession defect, resulting in the establishment of an aesthetically pleasing and healthy periodontium, with positive patient satisfaction. Significant root coverage was achieved through this procedure, demonstrating its clinical effectiveness.
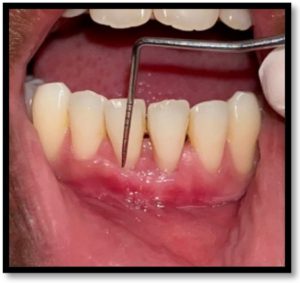
Among different surgical procedures, the Modified Coronally Advanced Tunnel (MCAT) technique has been studied to increase gingival dimensions and effectively achieve coverage of the denuded root surface area and enduring stability. The regular usage of Subepithelial connective tissue graft along with MCAT, has been suggested by many authors, which is considered as a standard means of building up the soft tissue to achieve the best coverage as possible of recessions and increasing the phenotypical width. Also, the muscular pull caused by insufficient vestibular depth can sometimes be a culprit behind the onset of gingival recession, which can be corrected by vestibuloplasty. Thus, in this case report, multiple gingival recessions were treated by Modified Coronally Advanced Tunnel (MCAT) technique with Sub-epithelial Connective Tissue Graft (SCTG).
Coronavirus has become a pandemic without a reliable treatment since December 2019. The antiviral medication remdesivir, which also inhibits one of the most powerful viral RNA enzymes, RNA dependent RNA polymerase, prevents the SARS-CoV virus from reproducing. Cardiomyocytes can experience substantial cytotoxic effects from remdesivir. Remdesivir binds to human mitochondrial RNA polymerase, which causes cardiotoxicity. A prolonged QT interval and the emergence of torsade de pointes could result from lengthening the field potential duration while lowering the amplitude of the Na+ peak and the pace of spontaneous beating in a dose-dependent way. The current safety profile of Remdesivir is not yet completely established, and it is necessary to evaluate the safety profile and any potential adverse cardiovascular consequences by conducting additional clinical trials. In this case report, adverse effects of remdesivir to assess its safety profile in Covid-19 patients is reviewed.


Lagophthalmos express the imperfect palpebra closure. It can be result as feelings like there’s commodity in the eyes, Ophthalmalgia, Epiphora or dry eyes, vague vision, red eyes, scleritis, light perceptivity, Insomnolence. Complete eyes close with a nictitation is important for maintaining a stable lacrimal layer and Healthy Eyes. Twenty years of girl visit to hospital with complaints of redness of left eye, Water secretion continuously specially with pain in left eye at night which was intolerable, severe light sensitivity, blurry vision, constant headache, not able to concentrate due to pain and blurry vision. Initially patient feels dry eyes during the day before a couple of day of starting continuously water secretion. On examination they conclude that patient eyes are not properly closed during sleeping which interpret in formation of stable tear film. After all examination they conclude that she has lagophthalmos. For management of her condition, she was prescribed with Optimoist Ultra 400 E/D, Moxiqua 0.5%. Lagophthalmos cannot be treated completely as the point so, Doctor suggests the lifelong therapy of this eye drops and eye gel for better outcomes and to prevent further symptoms flare. There should not be any surgical therapy in this case because lagophthalmos was detected in early stage within 2-3 weeks. According to guidelines if lagophthalmos is detected within 1-6 weeks then medical care therapy is sufficient to give better result. Lagophthalmos can be chronic if not treated early it can be causing complete and permeant vision loss