ABSTRACT
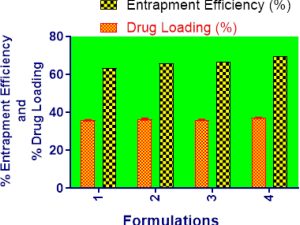
Background: This study focuses on the preparation and evaluation of Resveratrol loaded polymeric nanoparticles made of pegylated PLGA. Materials and Methods: In this study, both double-emulsion solvent evaporation and single-emulsion solvent evaporation were employed to formulate the Resveratrol loaded pegylated PLGA nanoparticles with PVA as surfactant. For the encapsulation of the hydrophobic drug Resveratrol, formulations were successfully prepared and tested for their particle size, polydispersity index, zeta potential, drug loading, and entrapment efficiency. Scanning electron microscopy was used to observe the morphology and surface characteristics of the nanoparticles. Using a sample and a separate method, an in vitro release study of the formulated polymeric nanoparticles was conducted. MTT assay was also used to determine the cytotoxicity of polymeric nanoparticles on breast cancer cells (MCF7). Results: The results demonstrated successful fabrication of the Resveratrol loaded pegylated PLGA nanoparticles. PVA was demonstrated in the present study to be a promising surfactant for the encapsulation and delivery of poorly water-soluble compounds as pegylated PLGA nanoparticles with the desired particle size, morphology, drug loading and entrapment efficiency. From the result of in vitro release study, it was observed that the optimized formulation showed 92.11% of cumulative percentage drug release which is higher than other formulations. Moreover, the optimized formulation demonstrated significant cytotoxic effect in MTT assay. The optimized nanoformulation showed 42.19% cell viability compared to the free Resveratrol at 66.59% cell viability. Conclusion: PLGA nanoparticles encapsulated with Resveratrol had been successfully used to deliver the drug to the target site by pegylated PLGA nanoparticles.
