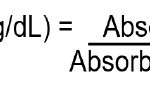INTRODUCTION
Since Steve Jobs introduced the iPhone in 2007, the sales of smartphones have expanded dramatically. The rise in smartphone usage is evidence of this. According to recent data, more than 6.6 billion people use smartphones worldwide to communicate, browse the web, or simply play video games.1 In recent years, the duration of smartphone usage has increased among most of the global population due to its wide range of applications.2 The excessive use of smartphones with associated dysfunction, withdrawal difficulties, and other phenomena similar to substance addiction is referred to as Problematic Smartphone Use (PSU).3 According to research on PSU, PSU is more likely to affect people who are young, female, and highly educated.1 PSU is defined as “smartphone use associated with at least some element of dysfunctional use, such as anxiety when the phone was not available, or neglect of other activities”.4 PSU is linked to various mental health conditions such anxiety, depression, and others.5 The excessive use of cell phones, often known as “nomophobia”, is a type of technological addiction that is quickly emerging as a serious social issue throughout the world.6
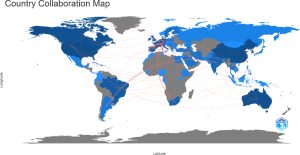
Healthcare-Associated Infections (HCAIs) pose a significant threat to the safety of patients and Healthcare Workers (HCWs). HCAIs increase morbidity and mortality, as well as healthcare costs. Therefore, prevention is a key goal for healthcare organisations and systems. In this regard, this study aims to conduct a bibliometric analysis of research and review papers published in journals indexed in the PubMed database between 2013 and 2023 on HCAIs in order to investigate areas of concentration and developing trends in the field. There was a total of 356 core zone publications, and the number of articles published is expected to reach its high in 2020. Most of the papers were found to have been published in the journals of hospital infection and antibiotic resistance and infection control. European countries conduct the most and more collaborative scientific research in this area, followed by the United States, Australia, and China. Surveillance, infection control, hand hygiene and COVID-19 represent the leading frontiers and research hotspots for HCAIs. HCAIs and Infection Prevention and Control (IPC) also co-occurred in most of the study discussions. The analysis is expected to yield meaningful data by illuminating the overall structure and direction of previous research on HCAIs, as well as by providing important ideas for future research.
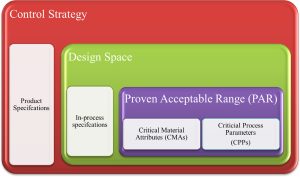
The Quality by Design (QbD) concept has been appreciated and expected by the regulatory agencies, especially the "United States Food and Drug Administration" (USFDA), the "European Medicines Agency" (EMA), and other agencies that have adopted the "International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use" (ICH) around the globe. This paper describes the application of QbD principles in the pharmaceutical development of Oral Solid Dosage forms (OSDs). It encourages the implementation of risk-based approaches when designing pharmaceutical products. It provides a thorough understanding of formulation variables, Critical Material Attributes (CMAs), process variables, and Critical Process Parameters (CPPs) based on industrial experience that can be considered for risk assessment during the development of OSDs. It provides handy guidance to academics, research scholars, and industry scientists for implementing QbD in developing the OSDs.
Fungal infection associated with eye annually affects more than one ten lakh people globally. It can affect vision and sometimes causes complete blindness. Drug delivery through ocular route has always been a challenge, as in the eye numerous barriers are located in conjunctiva, cornea, iris-ciliary body and retina which prevents drug dose from reaching the site resulting into low bioavailability of drug. Treatment through conventional dosage form often possess disadvantage of low retention time of drug as they are flows out from the corneal cavity by tear flow and nasal drainage. To overcome these challenges, the need of the hour is to fabricate a novel drug delivery system that would overcome the barrier channels of eye and could results into enhanced drug absorption at its site of action. Till date numerous technologies viz. Nanoparticles, Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC), Nano micelles, Microneedles, Liposomes etc have been developed. These technologies can overcome the barriers located in the eye and improve bioavailability of drugs. The present review highlights about nanostructured lipid carriers and their potential use in ocular delivery. The aim is to study nanostructured lipid carriers as nanocarriers to increase the permeability, solubility, bioavailability and retention time of active pharmaceutics agents through ocular administration. High-pressure homogenization, emulsification-solvent evaporation and micro-emulsion are some of the methods by which they can be prepared. So, it is concluded that nanostructured lipid carriers represent a potential nanocarrier for the reliable delivery of drugs to the ocular tissues with increased solubility, bioavailability and residence time.
The production of nanoparticles with the use of microbes is a technology that is environment friendly. This paper highlights the use of a syndicate of various micro-organisms (bacteria, actinomycetes, fungi, and algae) for the amalgamation of various metallic and metal oxide nanoparticles. When compared to physical and chemical methods, which are expensive, complicated, hazardous, and produce toxic wastes that are detrimental to the environment and the health of a variety of living beings, the synthesis of nanoparticles through the biological route is not only inexpensive, but also environmentally friendly, sustainable, and does not require a significant amount of energy to complete. This is in contrast to the fact that the physical and chemical methods are responsible for producing nanoparticles, which is an energy-intensive Nanoparticles can be biosynthesized via extracellular or intracellular pathways, depending on the particular circumstances. Capping, enzymatic reduction, and metal capture are the three steps that are involved in the process of nanoparticle production by micro-organisms. The organisms as well as the parameters that are utilised, such as temperature, pH and substrate concentration, all play a role in determining the size and form of the nanoparticles. The biogenesis of these nanoparticles takes place in a short amount of time and results in particles that have the right size and form. These nanoparticles are reliable and risk-free, and they have a wide range of applications in a variety of fields, including drug administration, cancer treatment, gene therapy, agricultural biosensors, the cosmetics sector, and many others.
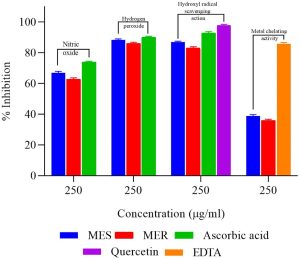
Background: In this present work, methanol extracts of the leaves and flowers of Salvia officinalis Linn. (MES) and Rosmarinus officinalis Linn. (MER) were examined for their potential anti-aging and antioxidant properties using in vitro methods. Materials and Methods: Several in vitro methods and techniques, such as estimation of reducing power, DPPH radical assay, ABTS decolorising assay, total antioxidant activity, superoxide radical (O2 • -), metal chelating activity, hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyl radical scavenging assay and assay of scavenging of nitric oxide were employed to appraise the scavenging of free radicals and antioxidant action of MES and MER. The anti-aging activity of the extracts was evaluated using the enzyme inhibition assays involving elastase inhibitory assay, collagenase inhibitory assay, and hyaluronidase inhibitory activity models. Using the elastase inhibitory assay, collagenase inhibitory assay, and hyaluronidase inhibitory assay models, the mechanistic antiaging potential of the extracts (MES and MER) had been appraised. Results: Because of their lower IC50 values, the extracts (MES and MER) showed significant antioxidant activity. It was discovered that they had poor metal chelating activity. By inhibiting elastase, collagenase, and hyaluronidase activity, both extracts showed significant anti-aging properties. Conclusion: The conclusions of this present research work thus imply that both the plant extracts possess the potential to act as antioxidant and may be used in herbal treatment for both normal and photoaging.
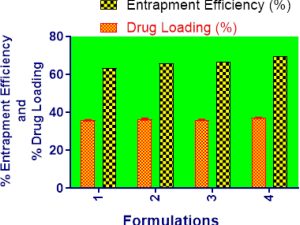
Background: This study focuses on the preparation and evaluation of Resveratrol loaded polymeric nanoparticles made of pegylated PLGA. Materials and Methods: In this study, both double-emulsion solvent evaporation and single-emulsion solvent evaporation were employed to formulate the Resveratrol loaded pegylated PLGA nanoparticles with PVA as surfactant. For the encapsulation of the hydrophobic drug Resveratrol, formulations were successfully prepared and tested for their particle size, polydispersity index, zeta potential, drug loading, and entrapment efficiency. Scanning electron microscopy was used to observe the morphology and surface characteristics of the nanoparticles. Using a sample and a separate method, an in vitro release study of the formulated polymeric nanoparticles was conducted. MTT assay was also used to determine the cytotoxicity of polymeric nanoparticles on breast cancer cells (MCF7). Results: The results demonstrated successful fabrication of the Resveratrol loaded pegylated PLGA nanoparticles. PVA was demonstrated in the present study to be a promising surfactant for the encapsulation and delivery of poorly water-soluble compounds as pegylated PLGA nanoparticles with the desired particle size, morphology, drug loading and entrapment efficiency. From the result of in vitro release study, it was observed that the optimized formulation showed 92.11% of cumulative percentage drug release which is higher than other formulations. Moreover, the optimized formulation demonstrated significant cytotoxic effect in MTT assay. The optimized nanoformulation showed 42.19% cell viability compared to the free Resveratrol at 66.59% cell viability. Conclusion: PLGA nanoparticles encapsulated with Resveratrol had been successfully used to deliver the drug to the target site by pegylated PLGA nanoparticles.
Background:
Wound healing is a complex and dynamic process of restoring cellular structures and tissue layers. The aim of the present investigation was formulation and optimization of instant film forming thermoreversible chitosan hydrogel for wound healing.
Materials and Methods:
A novel hydrogel composing of chitosan, Ethanol, Sodium α-β Glycerophosphate and combination of three drugs (Ascorbic acid, Tuftsin, Zn gluconate) were prepared. Ethanol and α-β Glycerophosphate (α-β-GP) were selected based on gelling time and film formation time. Optimization of vehicle in formulation was done by using 32 full factorial design using Design Expert® 8.0.7.1 software. Optimization of drug loaded thermoreversible chitosan hydrogel was done with 0.2mg, 2mg, 20mg, ratio of Zn gluconate, Tuftsin (10 μg/mL), Ascorbic acid (0.1mg/ mL) by trial-and-error method.
Results and Conclusion:
The Gelling time, Film formation time, swelling ratio and Moisture retention capacity of the optimize drug loaded formulation (X2) were 160±19.5, 390±18.4, 296±7.58, 6.8±0.76 respectively. The in vitro release of optimize drug loaded hydrogel formulation was carried out by Franz diffusion cell. In vitro drug release data of optimize batch was 86.5+1.9%, 80.66±4.52, 85.55±2.95 in 24 hr for Ascorbic acid, Tuftsin, Zn gluconate respectively. Chitosan hydrogel showed powerful antibacterial efficacy up to 100% to Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 29213) and Escherichia coli (ATCC 87064) by hydrogel formulation with or without drug. Since the formulation contains thermosensitive drugs stability study of optimized batch was carried out as per ICH guidelines. The stability data shows that the optimized batch of thermoreversible chitosan hydrogel remains stable for 1 month-controlled room temperature (25°C±2°C/ 60%RH±5%RH) and refrigerated condition (5°C±3°C). In vivo studies also carried out.

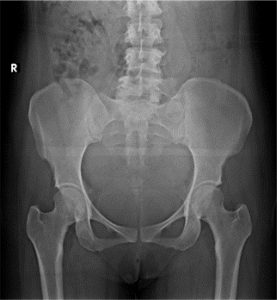
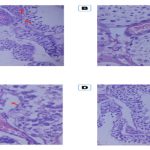
Background: Lumbosacral Transitional Vertebrae (LSTV) is one the common spinal anomalies encountered in patients with low backache. The aetiology of back pain is idiopathic, however low back ache causes substantial loss of productivity. LSTVs include various types such as Lumbarization, Sacralization, and the vertebrae with morphology such as complete fusion to the broadened transverse process. Low back pain associated with LSTV is due to anomalous articulation or may arise from the level above the transition, the contralateral facet when unilateral. Hence, the present study is planned to assess the prevalence of subtypes of LSTV in patients with low back aches and to determine the association of the different subtypes of LSTV with low back pain in a South Indian population. Materials and Methods: In this study, data was collected from 1000 patients of both sex in the age group of 15 to 90 years with complaints of low back ache attending the outpatient department of Orthopaedics of Saveetha Medical College, Chennai. The patients were sent to the Department of Radiology where radiographic images of the lumbar spine, anteroposterior view, and transverse view were taken. The patients were clinically and radiologically assessed and documented. Results: Out of the 1000 patients with complaints of low back ache, the incidence was more common in females (51.5%), than in males (48.5%). 155 patients in the study population showed imaging features of LSTV in which 24 (15.5%) showed Castellvi type I, 88 (56.7%) showed Castellvi type II, 18 (11.6%) had Castellvi type Type III and 25 (16.1%) showed Castellvi type IV. Out of these patients, type IA was observed in 13.1% and type IB in 2.5%. Maximum exhibited Castellvi type II in which type IIA was 22.2% and type IIB was 34.5%. Among Castellvi type III, 6.4% exhibited type IIIA, 5.2% type IIIB and 16.1% showed Castellvi type IV. Conclusion: Our study shows the association of LSTV type II with low back pain with more prevalence of low back pain noted in females. Therefore, LSTV should be considered part of the differential diagnosis of back pain, especially in cases of refractory pain.

Background: The most prevalent fungus infections that adversely affect people of all ages are called dermatophytoses. It is brought on by a particular class of fungus called ringworms, sometimes known as tineas, which includes the species Microsporum, Trichophyton, and Epidermophyton. About 20–25% of people worldwide have dermatophytosis. Direct contact with sick people can spread the disease, as can indirect contact with contaminated fomites. To determine the epidemiology, risk factors, clinical trends, and treatment profile of Superficial Fungal Infections, the current investigation was conducted (SFIs). Materials and Methods: A hospital-based prospective observational cross-sectional study was carried out at RIMS, Kadapa for six months, from November 2021 to April 2022. Based on the inclusion criteria, 120 patients were chosen. Data was gathered, examined, and summarized as averages. Microsoft Excel was used to represent the data using the graph pad prism programme. Results: In a total of 120 patients with tinea infections, we discovered that 45 were men and 75 were women; 64 patients are in the middle age group; 51 had BMI values below 18.5; 73 are illiterate; 15 have social habits; 60 are housewives; and 93 got Tinea as a result of towel sharing. In 87 patients with Tinea corporis, the upper and lower limbs were frequently afflicted; Trichophyton rubrum was isolated in 97 cases. There were 527 prescriptions total, of which 315 were for oral treatments and 212 were for topical treatments. Conclusion: Tinea corporis was the most common superficial fungal infection found in the GGH-RIMS. The most frequent species of Trichophyton isolated from patients with tinea was Trichophyton rubrum. Both the antifungal drug miconazole and the antihistamine drug CPM were widely prescribed.
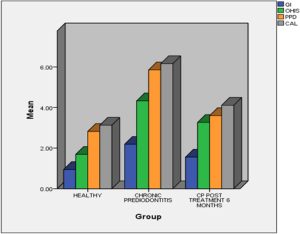
Background: There have been studies of associations between disease of periodontal tissues and disorders affecting the entire body for instance cardiovascular diseases, stroke, asthma, low preterm birth weight, rheumatoid arthritis, etc. An inflammatory biomarker, plasma Homocysteine, has been identified as a factor that increases the chances for developing cardiovascular diseases. Previous studies have implied that there may be an analogous correlation between the levels of plasma- Homocysteine and chronic generalized periodontitis patients in otherwise systemically stable people. The aim behind this study is to determine the levels of plasma-Homocysteine in patients with chronic generalized periodontitis before and after non-surgical periodontal therapy. Materials and Methods: 36 patients were selected from outpatient department of Periodontology, divided into 2 groups, Group A entailing of 18 healthy control individuals, and Group B comprising of subjects with chronic generalized periodontitis which is further subdivided into Group B1 which includes chronic generalized periodontitis patients at baseline, and Group B2, chronic generalized periodontitis patients 6 months after scaling and root planning. Clinical parameters recorded and blood samples of all the group subjects were collected for analyzing the levels of plasma Homocysteine. Results: The outcome showed significant differences in the mean plasma Homocysteine levels across the 3 research groups. Levels of plasma Homocysteine were significantly higher in Group BI, which declined after the scaling but not to the levels found among healthy individuals. Conclusion: The result indicates an early detection of periodontitis by analyzing levels of this biomarker. Also, non-surgical periodontal therapy may supplement traditional plasma Homocysteine lowering therapy.

Background: The standard treatment of type II diabetes mellitus (T2DM) more often explicitly decreased efficacy resulting in improper glycemic control. Hence, there is a need for alternative therapy like Gliptins, which play a key role in the management of diabetes mellitus. The current research studies the prescription pattern analysis of Teneligliptin in the therapy of T2DM patients. Materials and Methods: The investigation was a prospective observational study with a sample size of 302 cases in a diabetic centre in Erode, India. The patients were prescribed Teneligliptin along with Insulin and other oral antidiabetic drugs (OAD) and drugs for other co-morbid conditions. Patient details were collected in connection to prescribed medicines, biochemical lab data, other co-morbid conditions, and complications related to T2DM. Results: The prescription patterns of about 302 patients with T2DM, initially prescribed with gliptin, were reviewed. Teneligliptin was the gliptin drug prescribed along with insulin and other OADs. The commonly prescribed regimen was a combination of Teneligliptin, Metformin and Glibenclamide. Out of 302 patients, 169 were men and 133 were women within the age category of 50-59 years. The result of this study shows that the duration of diabetes and gender was statistically significant with p-value < 0.003 and 0.01 respectively. Conclusion: The analysis disclosed that the most repeatedly prescribed DPP4 inhibitor is Teneligliptin, mostly prescribed as an add-on therapy with metformin, insulin and other OAD drugs. Also, the current drug treatment and the planning of multiple drug interventions with changes in lifestyle for T2DM are much needed.

Background: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is a spectrum of conditions ranging from steatosis (without inflammation or fibrosis) to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis which is steatosis with necroinflammation associated with liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. The prevalence of a non-alcoholic fatty liver disease among health-screened patients in suburban medical facilities in Malaysia was reported at 22.7%. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with several complications that can be fatal. Objectives: This study was conducted to assess the awareness of the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease among pharmacy and medical students in a public university in Malaysia. Materials and Methods: The study was conducted through an online cross-sectional survey of 68 third-year students of both programs. The data obtained were initially analyzed through the Shapiro-Wilk normality test and since the data was found to be not normally distributed, the Mann-Whitney U test was conducted to analyze the mean with the level of significance defined at p<0.050. A chi-square test was also conducted to compare the variables involved. Results: The mean score obtained by participants in the third year of the pharmacy program was 9.28 CI 95% (8.60, 9.95) and the mean score recorded for participants in the third year of the medical program was 9.12 CI 95% (8.59, 9.65). Further analysis through Pearson’s Chi-Square test indicated no significant difference between the mean score obtained to the gender and race of the participants. Conclusion: The findings indicated that the score for the awareness of the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease among the respondents was moderate and there was no significant difference between the scores of the two different programs.
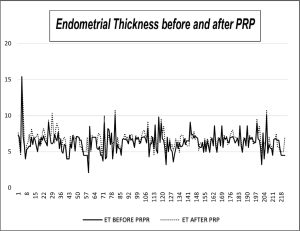
Background: Although various groups have reported the effects of intrauterine infusion of platelet-rich plasma, studies evaluating the effectiveness of injecting it hysteroscopically at the endomyometrial junction are limited. The latter has more effects on the angiogenic growth of cells. Platelet-rich plasma contains a high concentration of vascular endometrial growth factors and cytokines which are essential for endometrial proliferation. These are inadequately expressed in a deficient endometrium and are enhanced after its administration. The objective of the study was to assess the effect of subendometrial injection of autologous platelet-rich plasma treatment on endometrial thickness and vascularity on refractive endometrium during frozen embryo transfer. Materials and Methods: Data was collected from 232 women with endometrial thicknesses less than or equal to 7mm. Pre, post endometrial thickness and vascularity were assessed before and after platelet rich plasma administration. Results: Among 232 women, 8 were lost in follow-up. Among 224 women, endometrial thickness increased for 152, was not changed for 35, and decreased for 37. The mean endometrial thickness prior to infusion was 5.9mm which was significantly improved to 6.6mm after platelet-rich plasma infusion. Endometrial vascularity significantly improved for 124 women and decreased for 11 with no improvement observed in 89 women after platelet-rich plasma administration. Conclusion: Subendometrial administration of platelet-rich plasma has effectively improved the thickness and vascularity of endometrium thereby helping in pregnancy outcomes. Further in-depth molecular studies are required to interpret this therapy’s specific mechanism and beneficial role on the endometrium.
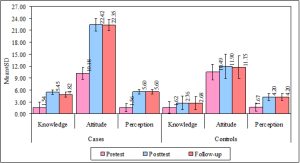
Background: Abuse of topical corticosteroids is a growing concern for dermatologists in India. It manifests itself in a variety of ways, most frequently on the face. Important underlying issues include a lack of public knowledge and the simplicity of acquiring topical corticosteroids without a prescription. There is a need to take urgent remedial steps and increase awareness about this problem in Health Science Student Population. Therefore, our study aims to assess and evaluate the Knowledge, Attitude and Perception (KAP) among health science student population regarding usage of topical corticosteroids. Materials and Methods: A Randomized case control study carried out among health science student population. A Self-prepared and validated KAP questionnaires were distributed to the health science student population through online forms and face-to-face interview were done after seminar was conducted in case group using audio-video visuals and only subject information leaflet is given in control group then post study was done after 1 month and follow-up after 3 months with the same set of questionnaires. Results: Out of 520 students women made up 69.23% more participants than men. The percentage of people aged 20 to 30 was 71.15%. Most of the participants were undergraduates with 81.15%. Pharmacy (22.69%) is the field with the highest enrolment, followed by Ayurveda, Nursing, Physiotherapy, Medical, dental and allied degrees. Case group showed significant improvement in KAP score respectively compared to control group (p<0.05). Conclusion: Educating with audio video visuals and seminar shows significant improvement in KAP scores compared to giving subject information leaflet.

Background: Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia (CDH) is a diaphragm abnormality it permits stomach contents to protrude into the thoracic cavity, posing a substantial risk for pulmonary and cardiac problems in newborns. The pathophysiology of congenital diaphragmatic hernia is a combination of lung hypoplasia and immaturity associated with Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension (PPHN) in newborns and cardiac dysfunction. Case Presentation: A 1-year-old male patient was admitted to the hospital with chief complaints of excessive crying, breathlessness, and fever for one month. On examination, we observed decreased air entry on the right side in the inframammary area, and no air entry in the infra-axillary area. The Ultrasonography (USG) of the chest showed bowel loops along with mesentery. Surgical correction is required for a diaphragmatic hernia. Right thoracotomy, laparotomy, and repair of hernia were done Conclusion: The Prior diagnosis during the pre-natal period induces a better prognosis.
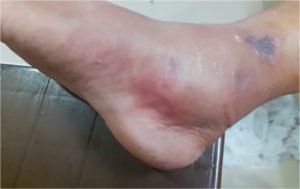
Presenting case report of necrotizing fasciitis, a rare bacterial infection, bacteria grow in the superficial layer of the fascia and release toxins, causing the infection to spread through the fascia. This is a serious disease that spreads quickly and requires immediate treatment. Compartment syndrome is one of the complications of necrotizing fasciitis. The prognosis is reliable based on clinical examination and assessment of intracompartmental pressure. Severe pain is important sign of this. Either the relatively rigid and closed muscle space, which is enclosed by fascia and bone, experiences bleeding and oedema. The case is unique in terms of the misdiagnosis and complication of the disease. Patient ageing forty-four years came to an emergency room with the complaint of pain, redness and severe swelling in right leg in the last 7 days. He went to a local hospital a week ago where cellulitis was diagnosed but before 2 days the swelling and pain got severe and so he came in as an emergency. It was noted here that he was misdiagnosed by cellulitis and so Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis (LRINEC) score was performed which revealed the intermediate risk of necrotizing Fasciitis. He was immediately admitted to operation room for surgical procedure called debridement with fasciotomy, after the surgery antibiotic treatment started and was continued for a week. Along with this, dressing of the surgical site was performed. Plastic surgery was done at surgical site after 15 days. With this treatment the recovery was good and the therapeutic goals were all achieved. So, it is better that this type of diagnosis should be identify at stage-1 to decrease the mortality rate.
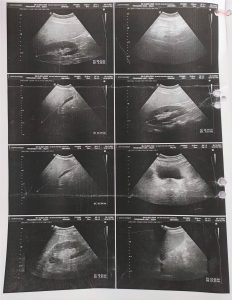
Anabolic androgenic steroids are a type of synthetic testosterone which are most likely used by athletes, body builders and physicians to increase male sex hormones in those who have not yet reached puberty. We present the case of 32-years-old male patient who was admitted in respiratory ward with complaints of breathlessness and weakness. Patient had history of left hydropneumothorax secondary due to pulmonary tuberculosis, iatrogenic cushing syndrome and was misusing anabolic androgenic steroids for muscle gain for a long time. The laboratory investigations were noted that elevation of liver function tests, abnormal haematological tests, ultrasonography was revealed to be hepatomegaly with grade II fatty liver. The patient was treated with the Dexamethasone, combination of Piperacillin and Tazobactam, combination of Metadoxine, Silymarin and l-Ornithinel-Aspartate (LOLA), Clonazepam, Ketoconazole and his health condition improved enough for him to be discharged. In conclusion we recommend the health care professionals to review the safety profile, examine laboratory results and counsel patients to prevent further abusage of anabolic androgenic steroids.
Background:
Albendazole is a bitter drug and a common antihelmintic drug with a wide range of effects due to its first-pass metabolism and limited bioavailability. It is available in oral dosage form to treat various intestinal illnesses. The goal of this study is to develop a new oral dosage form, a gelatin-based chewable, for pediatrics and devise a dosage form that is easier to take, tastes better, and does not smell strange.
Materials and Methods:
Gelatin (natural polymer used as gelling agent), sucrose and sorbitol, albendazole (active ingredient), citric acid and sodium benzoate, flavorant, and colorant were used. The study involves the formation of two separate solutions according to standard protocols. The first solution contained sorbitol, sucrose, and water 1:1, with a water-to-sorbitol ratio of 2:1. In order to make the second solution, water and gelatin were mixed and heated at 60°C. Both solutions were mixed, followed by the addition of other excipients.
Results:
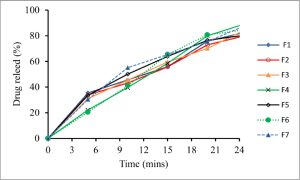
Preformulation studies involved bulk characterization and solubility analysis. Solubility analysis (pKa determination and partition coefficient) was carried out. Post-formulation studies were carried out to characterize the formulation, including in vitro disintegration and dissolution. A release kinetics study of the formulation revealed that these gummies followed first-order kinetics because it is an immediate-release formulation.
Conclusion:
The developed formulation of albendazole gummies was found to be similar to other formulations of albendazole available in the market in terms of physiochemical parameters and therefore can be produced as a generic formulation by an interested local pharmaceutical industry in the country.