ABSTRACT
Background:
Albendazole is a bitter drug and a common antihelmintic drug with a wide range of effects due to its first-pass metabolism and limited bioavailability. It is available in oral dosage form to treat various intestinal illnesses. The goal of this study is to develop a new oral dosage form, a gelatin-based chewable, for pediatrics and devise a dosage form that is easier to take, tastes better, and does not smell strange.
Materials and Methods:
Gelatin (natural polymer used as gelling agent), sucrose and sorbitol, albendazole (active ingredient), citric acid and sodium benzoate, flavorant, and colorant were used. The study involves the formation of two separate solutions according to standard protocols. The first solution contained sorbitol, sucrose, and water 1:1, with a water-to-sorbitol ratio of 2:1. In order to make the second solution, water and gelatin were mixed and heated at 60°C. Both solutions were mixed, followed by the addition of other excipients.
Results:
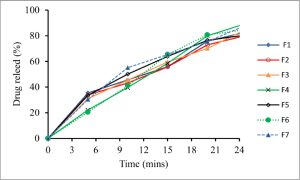
Preformulation studies involved bulk characterization and solubility analysis. Solubility analysis (pKa determination and partition coefficient) was carried out. Post-formulation studies were carried out to characterize the formulation, including in vitro disintegration and dissolution. A release kinetics study of the formulation revealed that these gummies followed first-order kinetics because it is an immediate-release formulation.
Conclusion:
The developed formulation of albendazole gummies was found to be similar to other formulations of albendazole available in the market in terms of physiochemical parameters and therefore can be produced as a generic formulation by an interested local pharmaceutical industry in the country.
