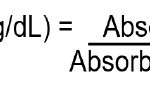Neuronal degeneration, characterized by progressive and irreversible loss of structure and function of neurons, could be a physiological age related or pathological intervention resulting in death of neuronal tissues. Neurodegenerative disease (ND) like Parkinson’s Disease (PD) and Alziemer’s Diseases (AD) aving molecular complexity in pathogenesis resulting in prominent loss of normal physiology of an individual. Practically, ND are incurable but by therapeutic approaches the loss of neurons and progress of disease is controlled but these drugs are associated with many unwanted effects. Herbals have been used from ancient times and referred to as conventional treatment methods to treat neurodegenerative disease having natural healing power and less side effects. Phytochemicals like Alkaloids, terpenes, saponins, phenols, flavonoids, etc. have major mechanisms behind management of most of the ND. In this review we briefly discussed some medicinal plants which have neuroprotective activities against ND specially AD and PD along with its mechanism of actions behind their pharmacological activities. Some herbal formulations used as traditional medicines to treat neurodegenerative disease worldwide are also briefly discussed.
Medicinal plants are a valuable source of supplementary remedies for the treatment of various ailments. Lawsonia inermis (belongs to family Lythraceae) or commonly known as Henna is a glabrous and branching small tree that is indigenous to the subtropical regions of Asia and North Africa. It has traditionally been used as a dandruff-fighting and antifungal agent when applied to the hair, hands, and feet. The staining properties of Henna are derived from the lawsone content, which is found primarily in the leaves. The purpose of this review is to conduct a literature search and critically review the relevant published articles on the phytochemical and pharmacological activities of L. inermis. The phytochemical screening reported that naphthoquinone derivatives, Henna essential oil, flavonoids, tannins, phenols, quinones, alkaloids, glycosides and saponins can be isolated from various parts of the Henna tree. The selection of appropriate solvents is critical in phytochemical screening, as different solvents resulted in different extraction yields. The pharmacological activities found in Henna are ameliorative activity, alleviating wound healing process, antifungal, antioxidant, antibacterial, hepatoprotective, nootropic, anti-ulcer, anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer activity. In conclusion, phytochemical screening is critical for identification of plants constituents, and Henna possesses wide range of pharmacological properties. As a result, further studies on Henna’s phytochemical and pharmacological qualities should be done to fully exploit its benefits.

Nature and health has always remained in consonance with each other. Various natural resources have got therapeutic purpose apart from their use in other industries. Clays from nature have been used frequently for therapeutic purposes from ancient times. The external use for stopping bleeding and their internal use for various ailments have been documented from early Greek civilization and Unani system of Medicine. Survey of literature from index journal, available Unani classical text, and authentic books and websites were carried out about therapeutic clays, their nomenclature, uses and rationale for their use was noted. Dioscorides has mentioned a number of clays in his book Materia Medica. Work of other Unani/Arab scholars AbūRayhān al-Bīrūnī, Ibn al-Bayţār, Hunayn Ibn Ishāq al- Ibādĩ Abū Bakr Muhammad ibn Zakariyyā al-Rāzī, Ibn Sīnā, Abul Qasim Khalaf ibn al-Abbās al-Zahrāwĩ on clays etc is been shortlisted in this work. Unani system enriched by vast literature extending from Greeks to Indian scholars bridged by the Medieval Arab scholars of medicine have left great legacy in regard to the description, use, and indication of various types of therapeutic clays, which are remedy for various diseases as a haemostatic, detergent, resolvent, astringent, wound healing etc, and also used as a cosmeceuticals and cosmetics. Present review attempted to enumerate the various aspects of different types of clays used in Unani system of medicine for therapeutic purposes.
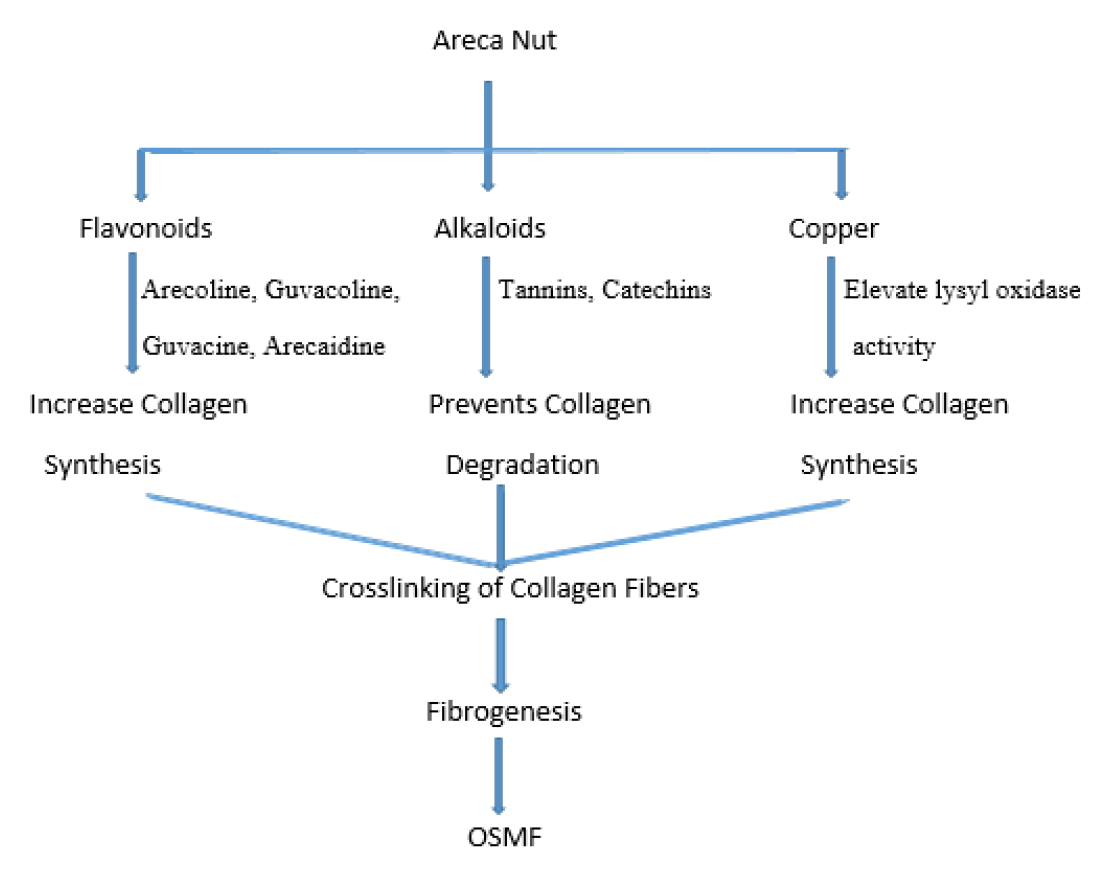
A fatal disorder named oral submucous fibrosis (OSMF) is marked by the oral submucosa’s progressive fibrosis. OSMF is distinguished by aberrant collagen deposition. In 1.5-15% of patients, it’s a precancerous condition that progresses to a malignant tumour. Although nutrient deficiencies and immunological procedures could perform a role in pathogenesis, epidemiological evidence suggests that betel nut quid (which contains guvacine, arecoline, guvacoline, arecaidine, and chavibetol) contains areca nut, slaked lime, tobacco, is a significant risk factor for OSMF. Submucous fibrosis, xerostomia, ulceration, a burning sensation, and a limited mobility of the mouth are among the symptoms. The patient’s quality of life is seriously affected by each of these components. The present article gives a broad overview of OSMF from a molecular viewpoint and describes what has been learned about its underlying causes, methods of diagnosis, and available treatments. Along with active therapy for OSMF, prophylaxis is essential, and this section gives a quick review of its treatment.
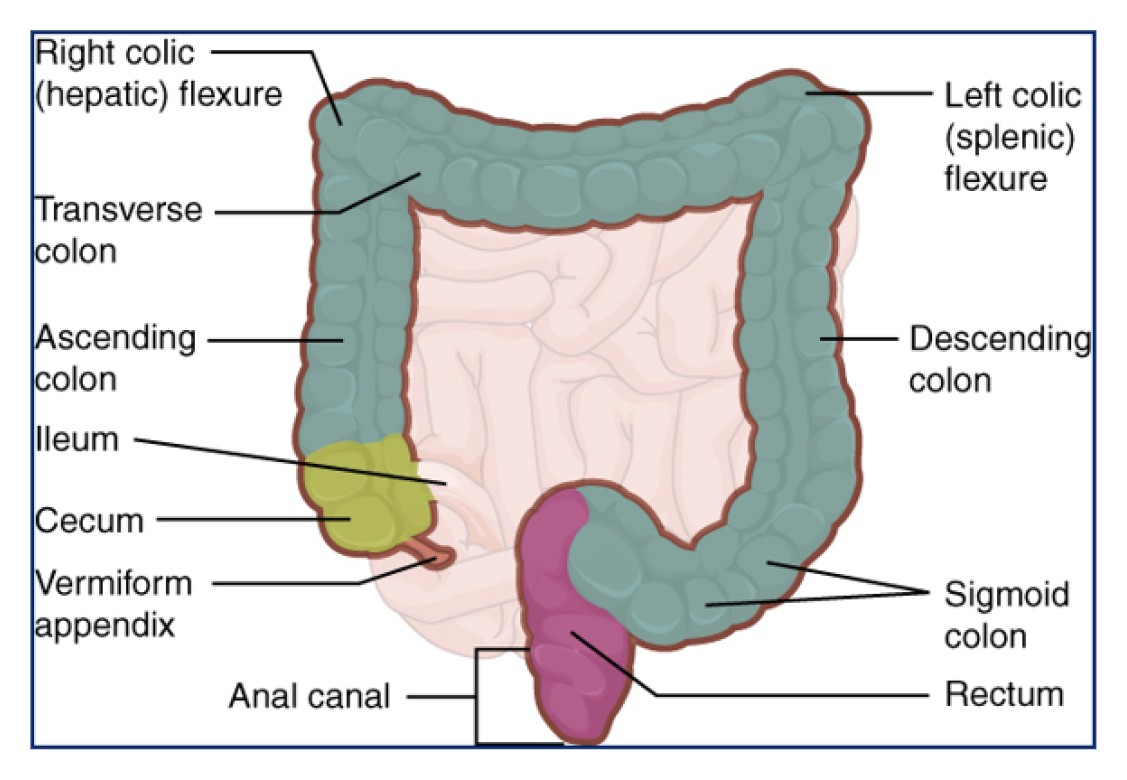
Compared to non-targeted medications, targeting drugs to specific sites of action has various advantages. Colon-designated drug conveyance improves the adequacy of therapeutics and empowers confined treatment. Because of this, it is a functioning space of examination for neighborhood sicknesses influencing the colon. The advances for planning oral medication conveyance have altogether expanded the bioavailability of medications to the colon and likewise worked on the remedial viability during infection. Presently a day’s nanotechnology assumes a significant part in oral dose plans as methodologies to additional upgrade take up into ailing tissue inside the colon. This exploration work manages the life systems and physiology of the colon, different methodologies for the colon focusing on, and assessment of medication discharge in the colon to give refreshed data for the need and improvement of medication stacked nanoparticles for various sorts of colonic infection.
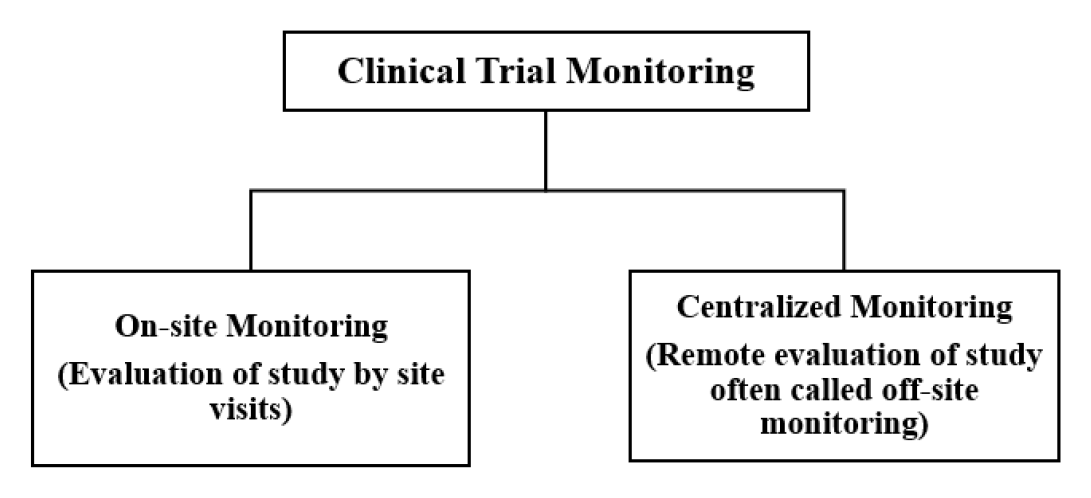
Clinical Trial Monitoring is the fundamental necessity to direct high-quality clinical research to guarantee research quality and subject protection according to regulatory standards. It is a sophisticated, innovation-based approach to utilizing a company's data, allowing for better-informed decisions regarding where and how to allocate resources. However, the monitoring plan is grouped into two kinds i.e., on-site and centralized monitoring. But recently, regulators have been urged to take on a risk-based monitoring system, as such sponsors are preferring centralized monitoring from the beginning of the trial. Risk-based monitoring assures the quality of trials by managing risks. Furthermore, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Medicine Agency (EMA) have embraced the risk-based approach and released a guideline paper on the subject. The FDA's proposed advice from 2013 discusses how to oversee clinical trials using a risk-based approach. Still, on-site monitoring, which is carried out by site visits, and centralized monitoring, which is carried out remotely or offsite, have their self-worth and advantages. Because of the greater complexity of grasping those monitoring procedures, in this review article, we will discuss both monitoring plans with an emphasis on centralized monitoring, which will aid in a better understanding of the entire in a nutshell. Also, we will emphasize the benefits, future, and implementation of Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning in the risk-based monitoring strategy.

Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a major public health ailment worldwide. The three main methods of treating diabetes are medication, diet therapy, and insulin therapy. However, these therapy not much significance due to their unavoidable disadvantages. Herbal drugs treatment is a noval strategy to treat DM (Type- II) due to their non-toxic effect. Fruit-producing herbal plants are crucial in the treatment of diabetes mellitus (DM). The main source of lipids, protein, dietary fibre, minerals, Vitamin E, mono-unsaturated fatty acids (MUFA), poly-unsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), arginine, and minerals is the oil of Perunus dulcis (almond). Carbohydrates, steroids, terpenoids, lipids, and other phenolic components were found in the oil upon phytochemical analysis.
In Albino Wistar rats, a single intraperitoneal infusion of streptozotocin (50 mg/kg) caused overnight fasting rats to develop Non-insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (NIDDM), after 15 min. of intraperitoneal administration of 100 mg/kg nicotinamide. If glucose level of rat is more than 200 mg/dL as Inclusion criteria in this study. In addition, enzymatic inhibition oxidative stress markers such as DPPH, H2O2 Radical Scavenging Activity Metal Ion Chelating Activity and Glucose Tolerance Test, Malondialdehyde (MDA), Reduced Glutathione (GSH), Catalase, and Superoxide dismutase (SOD) levels measured in liver tissue. Statistical analysis of carried out using one-way ANOVA was used to analyse the data, and then the Tukey post-hoc test.
Oil of kernals of Perunus dulcis (MILL) investigated against rats with Diabetes mellitus type II showed a significant reduction in (p<0.001) blood glucose level and inhibited key enzymes of carbohydrate metabolism i.e. α-amylase and α-glucosidase and also showed antioxidant activity.
The findings of this study reflect that oil had antioxidant activities which showed the excellent potential of oil which was comparable to standard. Antioxidants may have a crucial role in the treatment of Diabetes Mellitus Type II (T2DM), since oxidative stress is linked to the pathophysiology of diabetes.
The arial part of Asparagus officinalis (A.O.) (Family: Asparagus) stem and seeds, leaf parts of Mucuna gigantea (M.G.) (Family: Fabaceae) and fruit rinds and arial part of Garcinia travancorica (G.T.) (Family: Clusiaceae) have long been used to treat joint pain. However, its preclinical efficacy for rheumatoid arthritis has not been pharmacologically evaluated. In the current study, extracts of A.O.,M.G., and G.T. from petroleum ether, ethanolic extract, and aqueous extract were examined for their analgesic, anti-inflammatory, anti-arthritic, and phytochemical properties.
Rats’ tail flick method was used to assess analgesic activity, carrageenan-induced paw oedema model was used to assess anti-inflammatory activity, and protein Complete Freund's Adjuvant (CFA)-induced arthritis model was used to assess anti-arthritic potential.
We observed that many extracts had anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic effects, and to a lesser extent, analgesic activities corresponding to the administered dose. The CFA model's findings showed improved defence against arthritic lesions and changes in body weight. Additionally, rheumatoid factor, altered WBCs count, and histological and radiographic changes were all markedly improved by M.G., G.T., and A.O.
All the three plants extract when given together, supports traditional combinatorial use of M.G., G.T. and A.O. as potent analgesic, a potential anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic polypharmacy for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.

Dyslipidemia is a major public health issue in developed and developing countries, and it is a major risk factor for ischemic heart disease, atherosclerosis, and cerebrovascular accidents. The current trend is most of the antihyperlipidemic drugs like atorvastatin, fibrates, statins, nicotinic acid, probucol, and other chemical formulations were extensively used to treat hyperlipidemia clinically. The because of their serious adverse effects including diarrhea, nausea, myositis, and altered liver functions with statins and their use is restricted. Fragaria vesca is commonly consumed by the population in a routine lifestyle.and it has lipid-lowering properties Hence, the present study is planned to investigate the hypolipidemic activity of Fragaria vesca fruit extract on high-fat diet-induced hyperlipidemia in Wistar albino rats was studied.
In all groups except Group - I, a high-fat diet was given orally. The study included sixty-six male Wistar albino rats weighing 180-200 gm. After one week of growth, the animals were divided into eleven groups, each group contain six Wistar albino rats, and they were randomly assigned. Fragaria vesca fruit extractwas given orally and estimated body weight, lipid profile, and blood sugar levels were in all the groups before and after the induced fat model in Wistar albino rats.
According to the findings, ellagicacid (500mg/kg per oral for 4 weeks), Fragaria vesca (500mg/kg per oral for 4 weeks), tocopherol (500mg/kg per oral for 4 weeks), zinc oxide FV (250mg/kg per oral for 4 weeks), zinc oxide FV (500mg/kg per oral for 4 weeks) were effective into decreases Total Cholesterol, Triglycerides, and LDL and Increasing HDL in the management of hyperlipidemia.
The study concluded that the Phytochemical compound of Fragaria vesca showed a significant decrease in the levels of lipid profile Total Cholesterol, Triglycerides, LDL, and Increased HDL in high fat-induced hyperlipidemic Wistar albino rats.
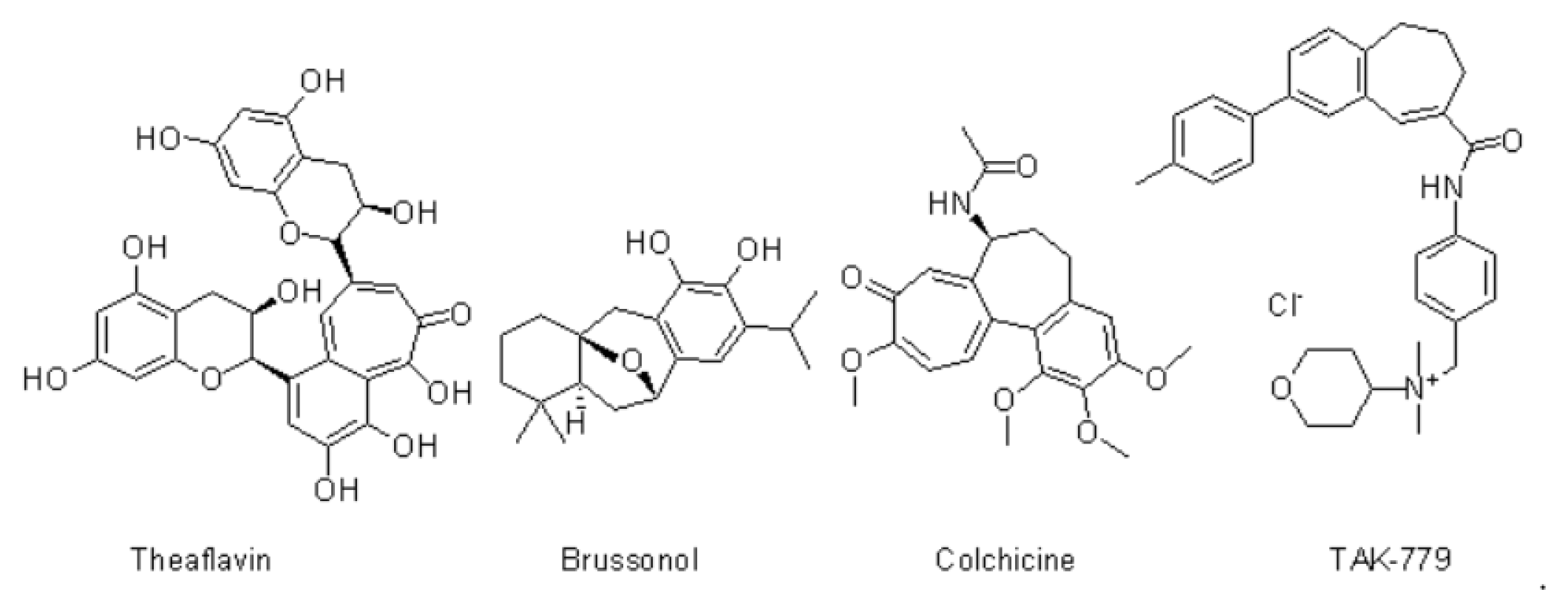
The core structure of benzo[7] annulene contains a number of natural products, and this moiety is helpful in the treatment of many pharmacological activities. The thiazolidine ring has strong antibacterial activity, multi-drug resistance in several bacterial strains, and it shows effective in pharmacological treatment.
A novel series of compound were synthesized 2-(9-chloro-2,3-dimethyl-6,7-dihydro-5H-benzo[7]annulen-8- yl)-3-thiazolidin-4one (9a-i) (10a-i) and its scaffold. All the synthesized compound are purified by using ethanol for recrystallization. The protein is download from PDB 5C5S (human myosin 9b RhoGAP) and it predicted in silico studies using Autodock Vina PyRx (0.8).
All the derivatives are characterized by TLC and spectral analysis 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, MASS. All the synthesized compounds were screened as in vitro anti-cancer, and anti-bacterial activity. Among the series of compound 9h, 9i, 10h, 10i exhibit more potent against two cancer cell lines MCF7, A549. IC50μg/mL 9h (21.16 and 19.26μg/mL), 9i (24.21 and 20.44μg/mL), 10h (18.32 and 16.32μg/ mL), 10i (17.46 and18.28μg/mL). with the reference drugs as doxorubicin (15.29 and 12.26μg/ mL) and also screened antibacterial activity most of the compound shows promising active with reference ciprofloxacin and the molecular docking analysis results shows a good binding affinity with 5c5s protein.
The synthesized compounds were screened in vitro evaluation of anticancer activity by using MTT assay and antibacterial evaluation of different bacterial strain by using agar diffusion method. The synthesized compound were show more active when carbon chain increases activity also increases.
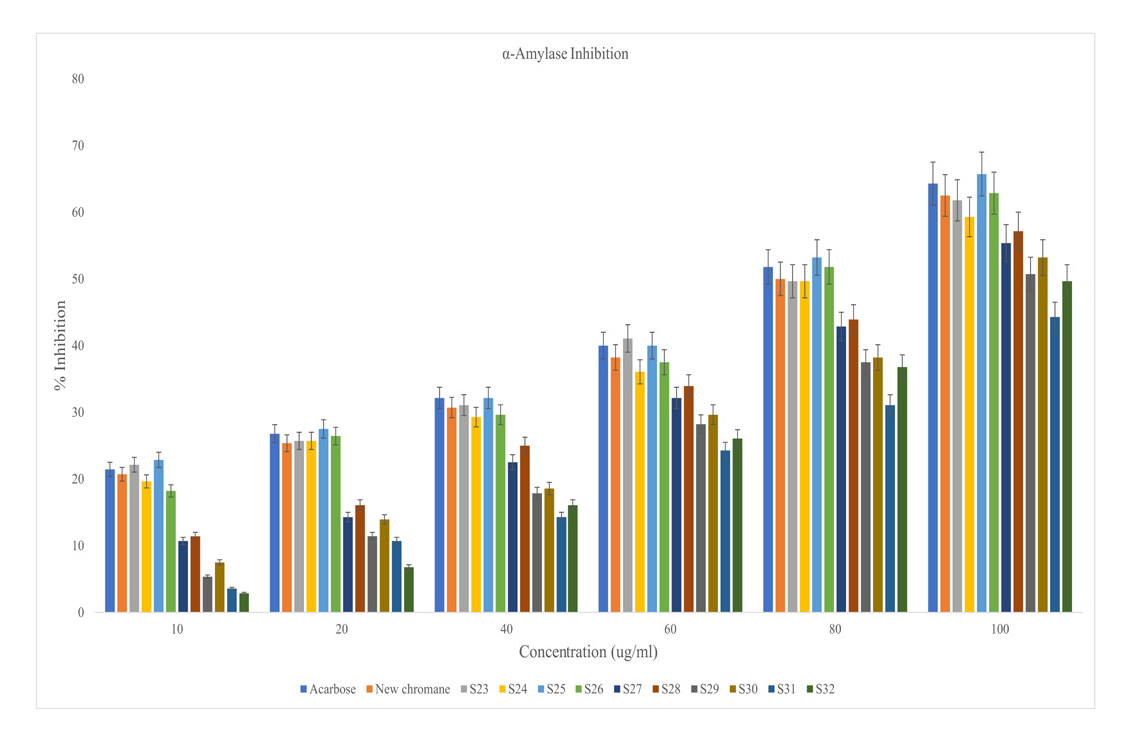
To evaluate biological activity of synthesised new chromane and its analogues.
New chromane {3,5,7-trihydroxy 2-(4-hydroxy benzyl) chroman-4-one} isolated from dried leaves of Dillenia indica Linn., family Dilleniaceae is structurally relating with various reported chroman-4-one derivatives displaying remarkable in vivo antidiabetic activity. But the literature reveals that 0.8 - 1.0% yield of pure new chromane was obtained in isolation. Following reported literature data of synthesis and in silico study; Synthesized new chromane and its derivatives (S23-S32) were investigated for in vitro (α-amylase and α-glucosidase) as well as in vivo antidiabetic evaluation respectively.
in vitro hypoglycaemic study also displayed the significant antidiabetic potential of new chromane and its O-alkyl substituents (especially S23) while other synthesized compounds (S27-S32) reported for moderate to mild effects w.r.t. reference drug (acarbose). Moreover, synthetic new chromane and O-alkyl substituent (S23) exhibited maximum antidiabetic activity also in terms of lowering glucose concentration while others (S27-S32) showed mild anti-diabetic effect in comparison to reference drug (metformin).
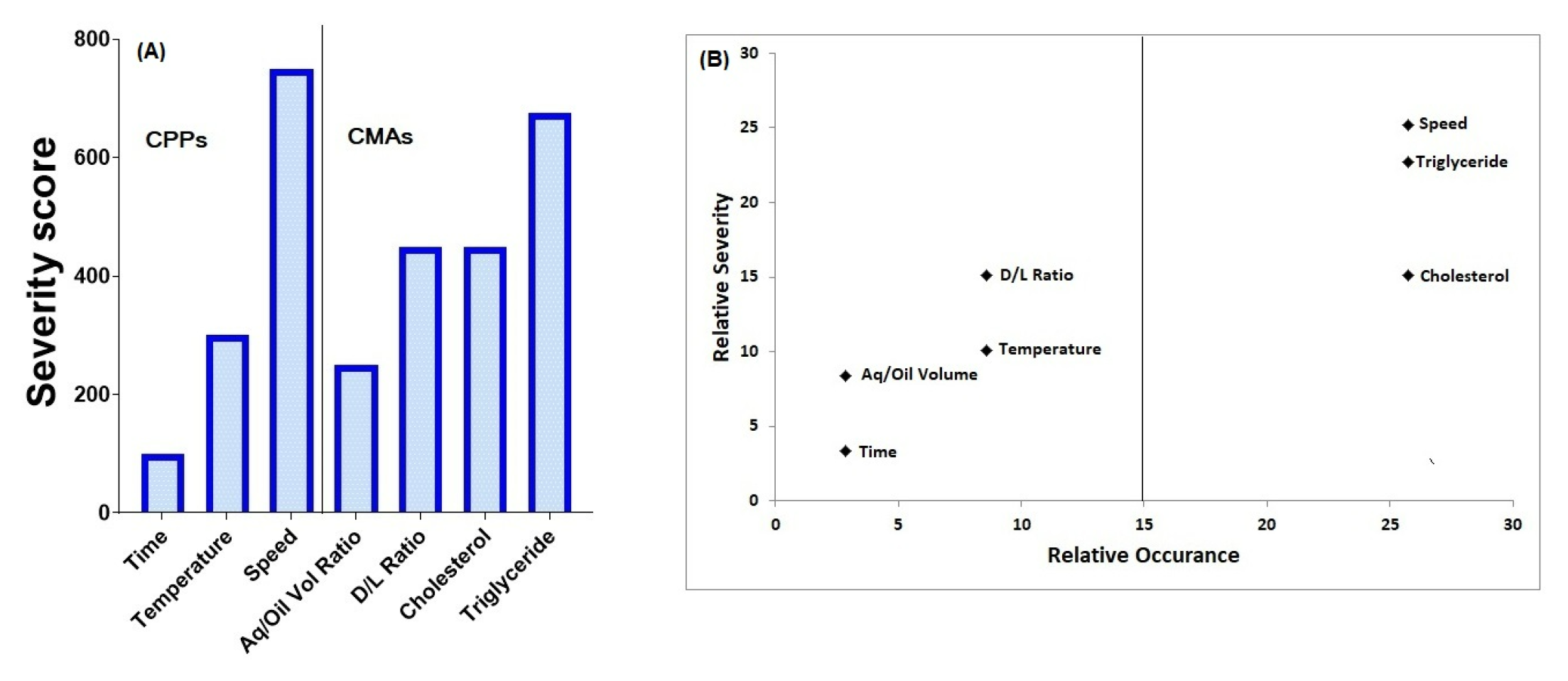
Dexmedetomidine is a promising candidate for pain relief and is being evaluated as an alternative or adjuvant to other treatment modalities. The intraarticular administration of such drugs is expected to give localised effect and the release of drug from drug delivery systems can be programmed to lengthen the duration of action.
The aim of the present investigation was to develop dispersion of lipospheres for the Dexmedetomidine for intraarticular administration that releases drug over a period of one week.
DEX-LPS were formulated using the multiple emulsion technique. The particle size of lipospheres, drug entrapment, and percentage of drug release qualified as critical quality attributes. Risk assessment was done for the material attributes and process parameters based on the quality by design principles. The amount of cholesterol, triglyceride and the speed of homogenization during the primary emulsion formulation were identified as critical variables and therefore studied systematically using a Box-Behnken Design. Mathematical models generated for each critical quality attribute and their relationship with predictors was explored, using RStudio, to get a product that had the largest particle size, highest entrapment and desirable drug release profile.
Overlay plots were generated and the formulation at the center point settings had the required desirability. The acceptance range for the in-process and end-product quality attributes was established and tested in the product. The product remained stable at 2-8°C during 6 months of study.
Stable DEX-LPS that could sustain drug release for 7 days was developed.
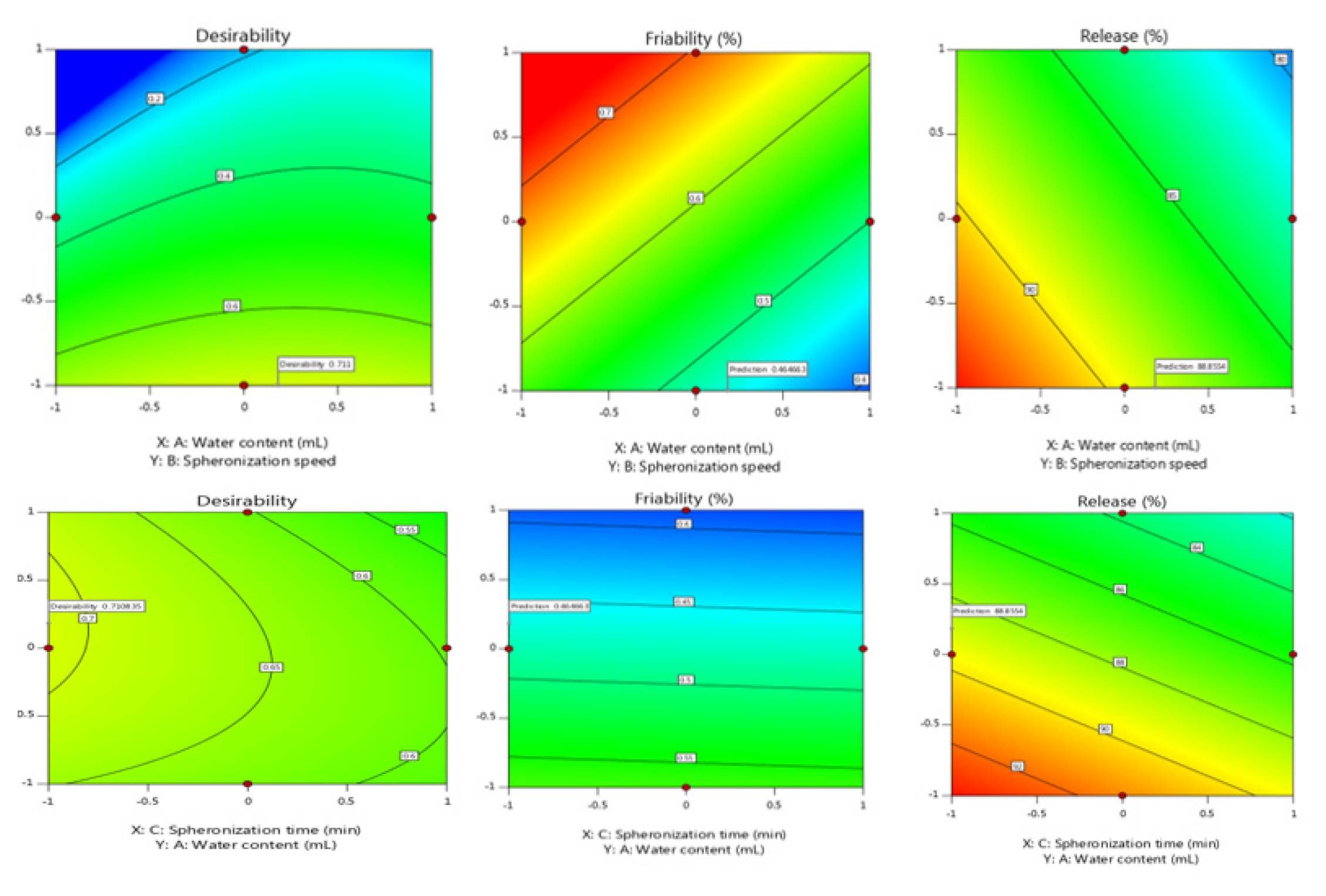
The main goal of any drug delivery system is to achieve the desired concentration of the drug in blood or tissue, which is therapeutically effective and nontoxic for a prolonged period. Sitagliptin is a dipeptidyl peptidase 4 enzyme inhibitor used in the treatment of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. The purpose of this study was to design a flexible dosage form that controls the release and provides therapeutic effects with minimum side effects.
Various batches of pellets were made using the extrusion spheronization technique for obtaining the batch that resulted in a sustained release pattern for Sitagliptin.
The pellets showed excellent flow properties due to sphericity thereby influencing the dosage production rate, the small particle that could easily disperse and help in avoiding the dose dumping. The pellets showed 89.10 % release in 12 hr.
The study concludes the development of sustained-release pellets by selective excipients with better drug release minimizing the problems.
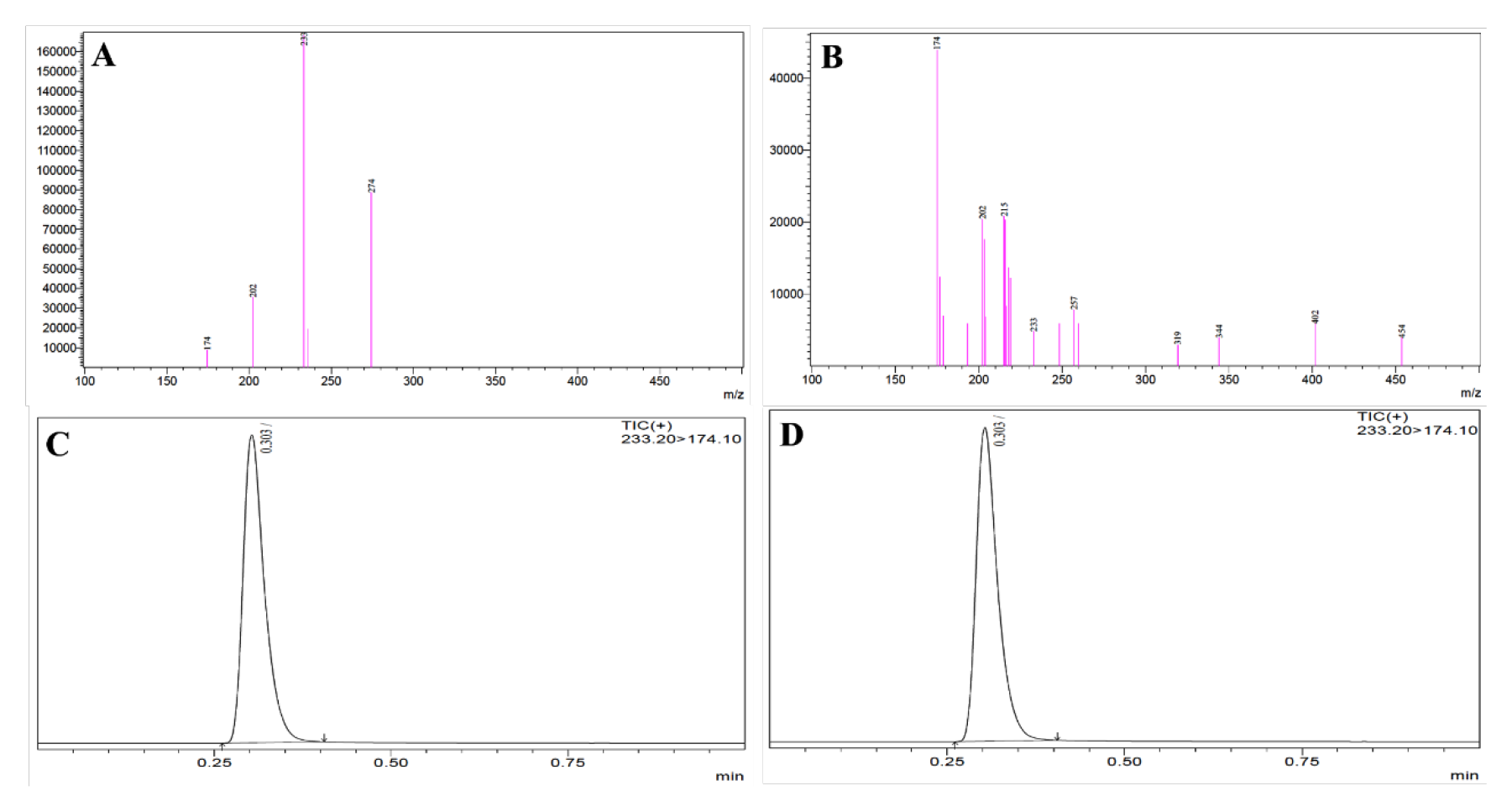
To develop a first-time-novel polymeric NPs from PLGA and their coating by Chitosan (CS) of Melatonin (MT) for the enhancement of lungs bioavailability by targeting lungs from the nose.
The Melatonin LC-MS/MS method was developed for the first time for a comparative Pulmokinetic evaluation administered by different routes which will be useful for the treatment of lung cancer and in vitro evaluation on lung cancer cell-lines (H1299). The solvent evaporation method was used to develop the PLGA nanoparticles and their encapsulation by CS.
CS MT PLGA MPs were given a significantly high release and permeation of MT as compared to MT PLGA NPs. Different routes of administration were used to compare the pulmokinetics parameters. Lung cancer cell lines (H1299) were used for anticancer activities. PDI, ZP, PS, DL, and EE of CS MT PLGA NPs were observed at 0.131±0.009, +19.5±1.37mV, 98.36±7.15 nm, 4.19±0.38%, and 74.16 ± 5.29% respectively. Mucoadhesive nature of CS MT PLGA NPs was showed greater than MT PLGA NPs and MT S with 0.303 retention time with mas’ spectra of 233.20/174.10. The developed method was linear (1-1000ng/mL) with inter and intra-day accuracy (91.68-98.95%) followed by precision (1.67—2.69%). Cmax and AUC0-24 were significantly enhanced (p<0.001) than i.v. and oral in the lungs.
Capping of CS on PLGA NPs could be a strong possible nanocarrier for Melatonin to enhance their solubility of a drug (MT), entrapment, sustain and controlled release, and stability, with their therapeutic application.
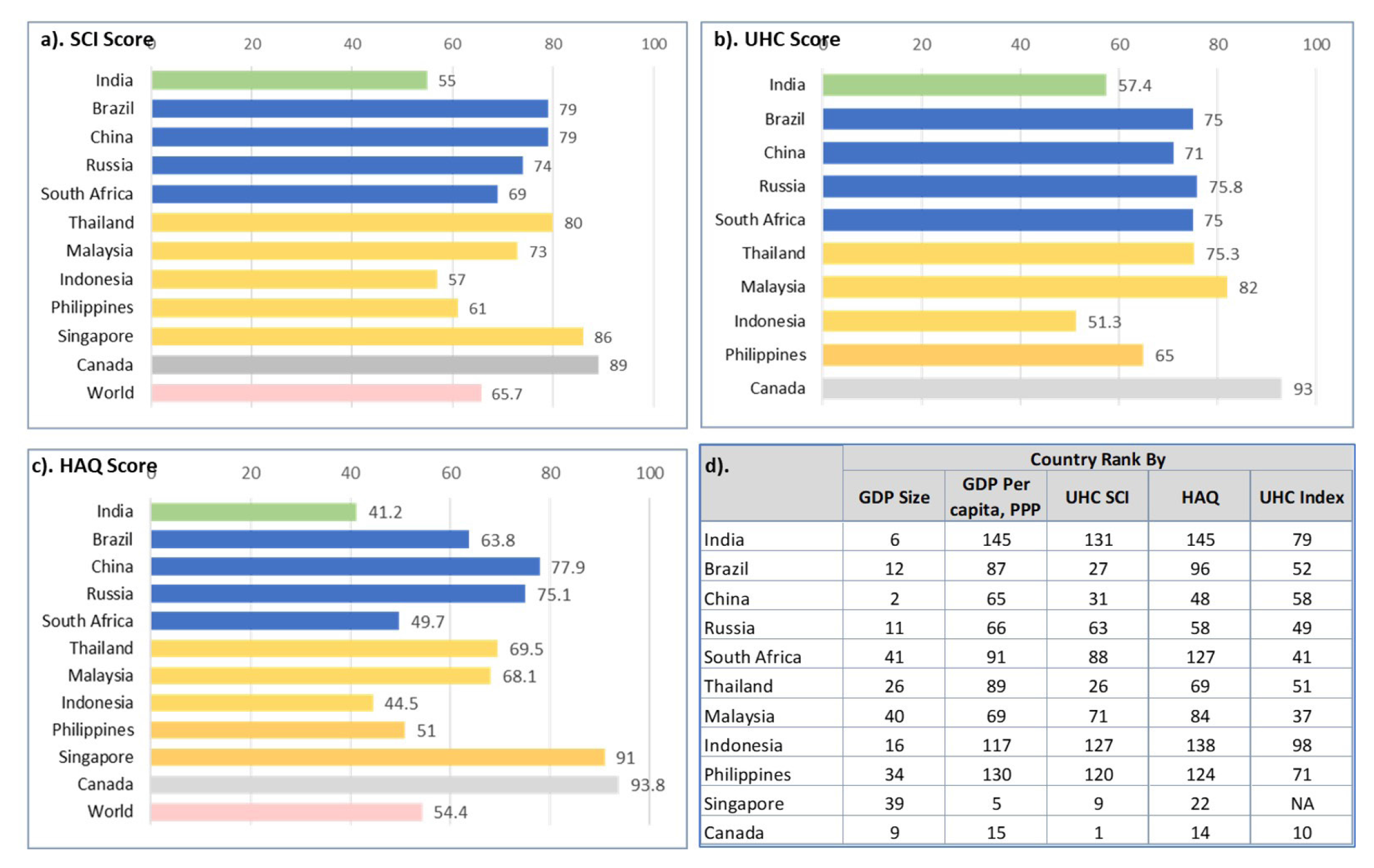
India has shown remarkable progress on several health parameters and a political will to usher in Universal Health Coverage (UHC) framework as defined by the global sustainable development goal 3.8. Given myriad challenges of a fast-growing economy with a massive population, how India fares on this goal is important not just for the country but also has implications at the global level. This research is a comparative analysis of progress made by India towards UHC vs. peer economies from BRICS and ASEAN-5.
Three performance indicators were selected through a comprehensive review of research in the area, namely SCI (Service Coverage Index) for “access”, HAQ (Health Access and Quality) for “outcome”, and UHC index for a composite indicator of “access and financial protection”. In addition, financial protection parameters of out-of-pocket expenditures and consequent impoverishment were also considered. These indices measure distinct aspect of UHC, but none covers the full spectrum of success criteria, hence we used cross-tabulation technique for a holistic comparison.
Despite significant progress on various health indicators, India lags behind its peer economies of BRICS and ASEAN-5 in achieving UHC goal. A deficit in infrastructure and trained health-workforce continues to undermine efforts to provide healthcare to all, complicated further by inequitable distribution of these resources.
Pharmacists have an important role in improving access to healthcare by playing a more active role in preventative care, patient counselling and disease management, thus supporting India’s ambitious journey towards achieving UHC for its over 1.3 billion citizens.

During literature review a multiple factor comes to the light which are responsible for medication Non-adherence. On the bases of that factors particulars questions are framed and a scale is developed to assess medication adherence and factors leading to non-adherence. On the bases of assessment pharmacist can counsel the patient for better therapeutic outcome in chronic disorder and also particular factors can be focus for effective counselling.
Scale is been validated and will used to assess patients in chronic disorders like rheumatoid arthritis, hypothyroidism, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in tertiary care hospital. After assessment pharmacist can counsel the patient to improve medication adherence.
Different scales are available for adherence assessment with number of limitations and lacks. In attempt to overcome these limitations new scale has been developed considering all the affecting factors for non-adherence and possible askable question to determine factors.

The Medication Regimen Complexity Index (MRCI) is a reliable tool to evaluate the complexity of pharmacotherapy and can predict the treatment adherence of post-transplant patients. The MRCI was evaluated in the post-kidney transplant period.
In a descriptive, observational, and cross-sectional study, we evaluated the pharmacotherapy and the MRCI of kidney transplant patients for a year in a kidney transplant outpatient clinic at a university hospital in Fortaleza, Brazil. A convenience sample was obtained and analyzed the records of kidney transplant recipients who had at least two visits with pharmacists. The main outcome measures are characterization of immunosuppressive regimen, MRCI score, correlations between MRCI score and a period post-transplant.
109 patients were included in the study. The predominant class was antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents (27.7%), and the most frequent immunosuppressive regimen was tacrolimus, mycophenolate sodium and prednisone (63.30%). The mean points in MRCI were 46; minimum of 19 points associated with 3 drugs and maximum of 83.5 points with 16. About sections A, B and C of the MRCI, the means found were 2.60, 13.2 and 30.6 points, respectively. Correlations between MRCI score and number of medications were checked, and a period less than 180 days after transplantation had score >40 points.
MRCI in the kidney transplant patient is linked to the number of medications, dose and additional instructions. To improve adherence to the treatment, patient orientation is necessary especially in the first year after transplant.
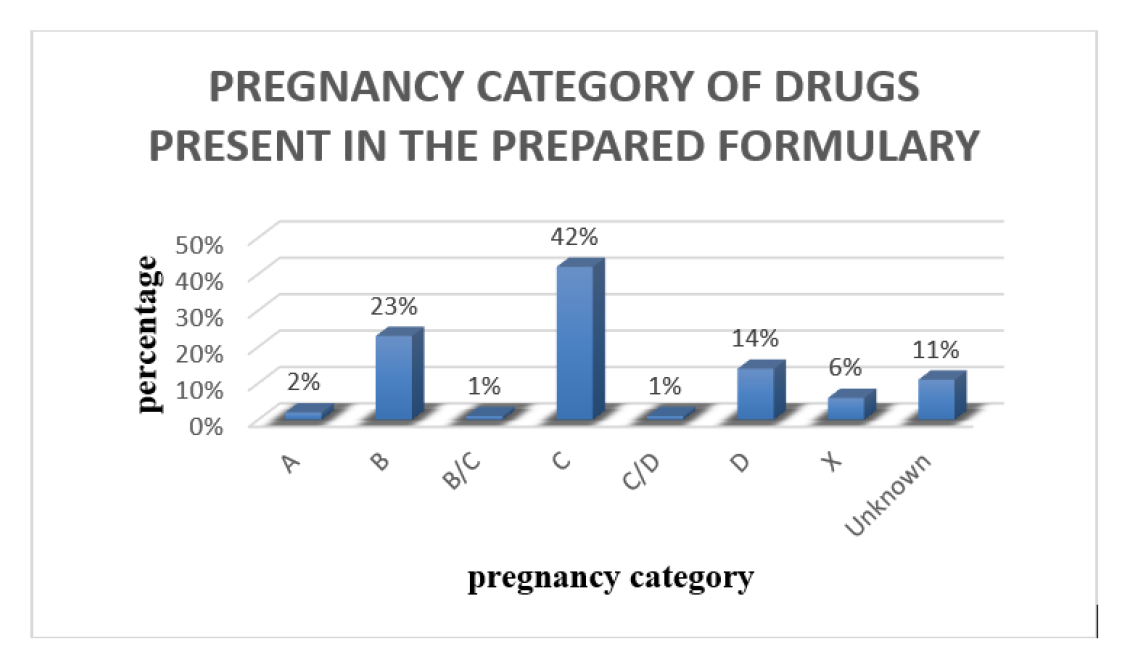
The important motive for creating a formulary is to set standards for great practice, merchandising high quality evidence-based prescribing, consequently, reduce the variant in degree of treatment furnished to the patients and controlling drug cost. Addition of drug to formulary is based on measures like safety, efficacy, quality and including drugs that are economically available for all types of patients. Routine therapeutic class review is necessary to standardize the formulary. Reviewing and evaluating all the therapeutic class of drugs and a new drug having an advantage over the current medicine is analyzed and included in the formulary. On the whole, the formulary helps to improve therapeutic outcome in a standardized manner and guides health care professionals in the rational prescription of drugs.
This study is a prospective study. The 4th edition was prepared by formulating a drug list that was standardized according to the WHO guidelines. Then the prepared formulary was compared with WHO 2019 and NLEM 2015. Preparation of a new edition was notified prior, and a well-prepared questionnaire was distributed among the physicians and other health care providers for their opinion and feedbacks.
While comparing the prepared formulary with NLEM and WHO, we found that a greater number of drugs were included in the prepared hospital formulary which reflects the advanced clinical set up of the hospital.
The study thus proves that timely standardization of formulary is essential for providing evidence-based medicine. A copy of the newly prepared formulary was circulated among different departments.
Success after liver transplantation involves different particularities. As important as the surgical procedure is the need for health information for patients, fundamental educational strategies facilitate the understanding of the guidelines provided by the health team.
To describe the process of elaboration and validation of an educational booklet for a liver transplant recipient.
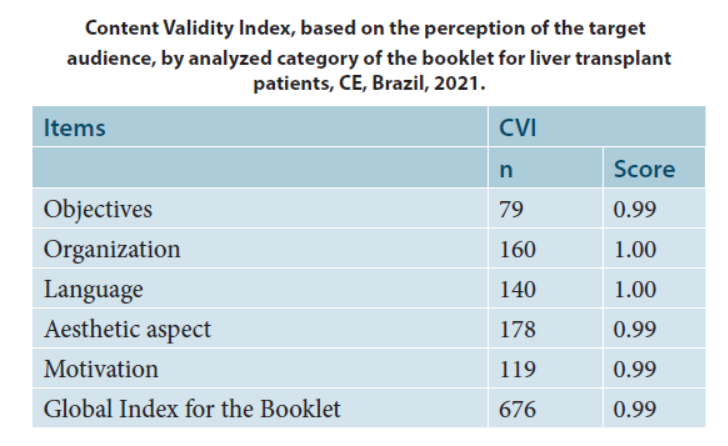
Methodological research, for the elaboration and validation of an educational technology, developed in three stages: bibliographic survey, elaboration of the booklet and validation of the material. Validation took place between May and August 2021 with professionals from the care team and patients from a specialized outpatient clinic of a university hospital. To analyze the validity, the Content Validity Index (CVI) and the Research Electronic Data Capture (REDCap) program were adopted for data storage and analysis. Results: The CVI obtained with the 17 expert judges was 0.98, and with 20 patients, 0.99, which proves to be valid material.
The booklet is valid and adequate for information to transplant patients, suggesting its implementation in the post-liver transplant routine as a guiding resource for care in order to make the process more effective.

Asthma is a chronic disease and one of the most familiar long-term respiratory diseases affecting millions of adults worldwide. High utilisation of healthcare resources in treating asthma and limited resources allocated to the disease has imposed the use of Pharmaco-economics evaluation methods such as cost-effectiveness analysis in healthcare decision-making. Hence, the present study is planned to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of corticosteroid preparations used in treating asthmatic patients at Alshaab Teaching Hospital (ASH) Khartoum, Khartoum State, Sudan.
A hospital-based cross-sectional design, whereby the cost and outcome of corticosteroid preparations were collected together. One hundred and thirty-nine adult asthmatic patients were systematically selected as the sample size. The data were collected using EQ-5D-3L Arabic version questionnaire and data collection forms and analysed using Statistical Package for Social Sciences (IBM) version 24.0.
In this study, out of 139 patients, the majority of them (58%) were females, fell within the 16-40 age group category (38%) and were married (82%). Our findings showed that the Symbicort inhaler was the most expensive preparation with an Average Cost-Effectiveness Ratio (ACER) of 3,283.10 SDG ($4901) per treatment. Prednisolone tablet was the least expensive, with an ACER of 643.40 SDG ($ 96) per treatment, the most reasonable alternative concerning effectiveness, and the most efficient preparation concerning effectiveness-adjusted costs.
This study concluded that the prevalence of asthma and utilisation of pharmaceutical products and services among adult asthmatic patients in ASH was higher in females (58%) and those in the 16-40 age group. The Symbicort inhaler was the most expensive preparation, and the Prednisolone tablet was the least expensive and most cost-effective of the three preparations evaluated in ASH.
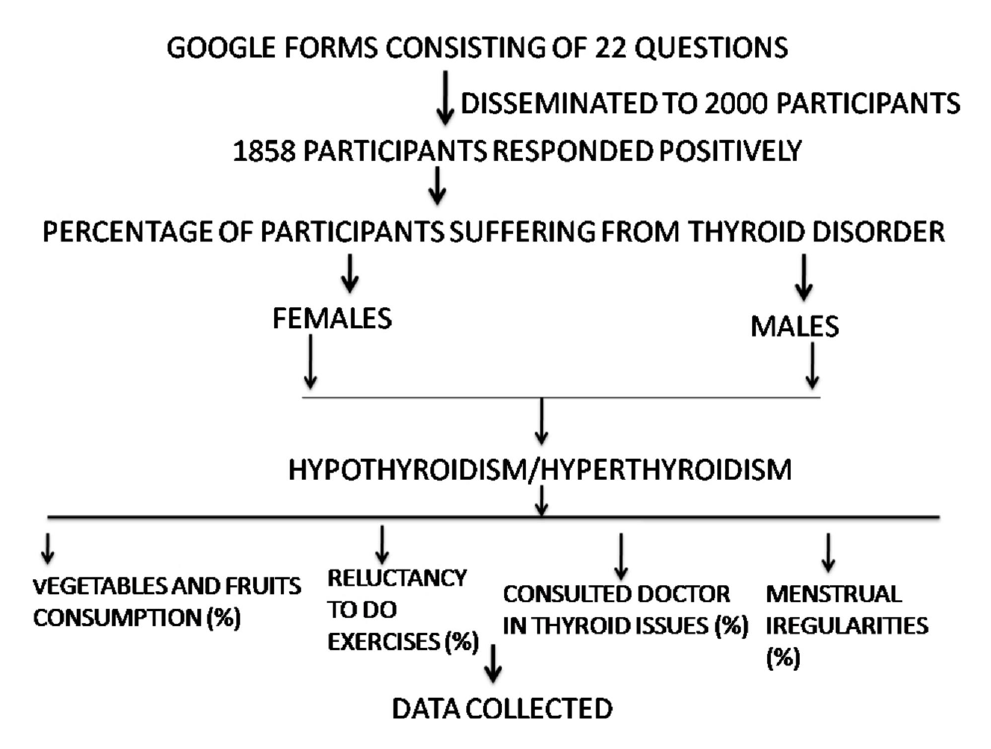
Thyroid disorder is becoming increasingly common in India. Thyroid disorder affects around forty million people in India. The number of cases in Telangana is increasing at an alarming rate. This survey aims to investigate the causes of an increase in thyroidism cases and to present data for debate at a thyroid problems symposium.
The current online survey has been conducted by posing 22 questions regarding the type of thyroid disorders and the predisposing factors responsible for it by distributing online Google forms randomly to a large group of the Telangana population which includes 2000 individuals.
The results obtained from the survey indicated that the most common thyroid disorder prevailing in Telangana is Hypothyroidism. Females are affected most with hypothyroidism to an extent of 62.3%. The cases of Hypothyroidism in pregnancy were found to be less (27.4%) in comparison to non-pregnant females (72.6%). Vegetables and fruits were found to be included very less in their respective diets (16.9%). Majority of the Hypothyroid patients have shown disinterest (68.4%) in performing exercises during Hypothyroid episodes. In many female hypothyroid participants, there are menstrual irregularities. TSH estimation remains the most popular test among the thyroid patients.
The outcome of the current survey suggests that there is a need to maintain a healthy diet which includes fruits and vegetables and regular exercises to maintain a healthy BMI. Females are advised to focus on the menstrual irregularities due to Hypothyroidism. If the above suggested measures were taken, then the hypothyroidism can be effectively controlled in Telangana where the incidences are alarmingly high.
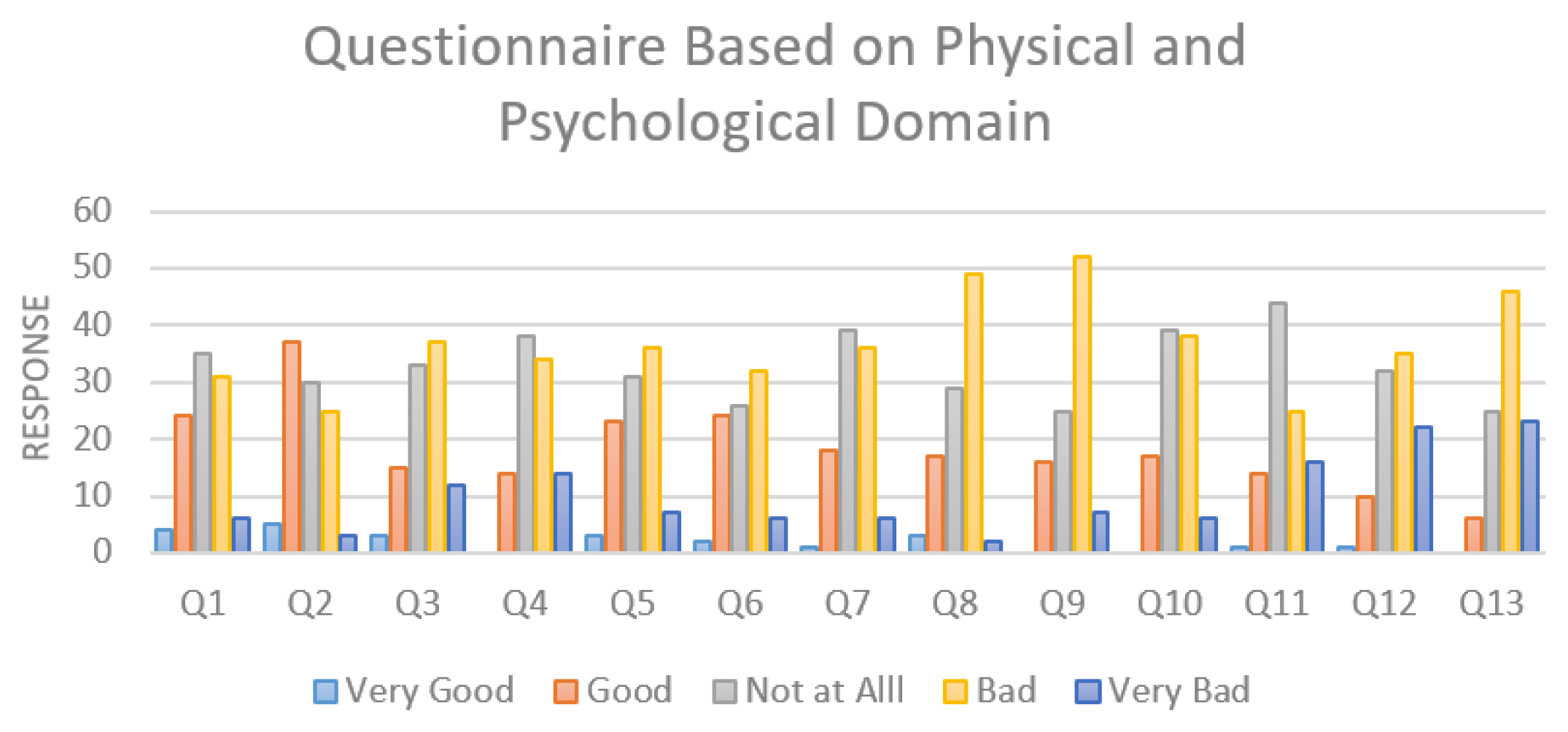
As a public health concern, hypertension is becoming higher prevalent among the elderly, making it a major problem in across India. Since physicians, scientists, and policymakers have realized the importance of the patient’s self-rated experience, beyond or in addition to objective and clinical measures of health, HRQOL improvement has risen to prominence in health research.
To study the effect of physical and psychological factors on HRQOL in patients suffering from hypertension using WHOQOL-BREF questionnaire.
A hospital-based observational study was conducted among hypertensive patients (aged 30 and older) in a teaching hospital enrolling IPD and OPD patients. Patients were interviewed for Quality of life (QOL) using WHOQOL-BREF questionnaires. Data were analyzed using graph Microsoft Office. The statistical analysis (mean and standard deviation) involved a descriptive analysis, and the results were shown as absolute numbers and percentages.
It was observed that the physical domain’s mean score was higher than the psychological domain’s [56.623 ± (SD 0.2274) and 54.875 ± (SD 0.5413), respectively] indicating an inverse relationship between low quality of life and low mood, anxiety, and depression. In response to individual questions, the majority of participants reported experiencing moderate pain, being content with their daily activities, feeling full and able to concentrate, and having negative thoughts.
A higher quality of life was found to be positively connected with male gender, older age (60-69 years), negative emotions, and lack of education, but not with female gender, older age (60-69 years), primary education, or negative emotions. Thus, in hypertension patients, each of these characteristics is a significant predictor of the quality of life associated to their health.
Essential oils are the plant secondary metabolites, which are a complex mixture of flavoring volatile compounds. The biosynthesis of these volatile compounds by the plant is intended for chemical communication. They largely meant for activities like antimicrobial, cytoprotection, antioxidant and insect attraction to assist pollination. Essential oils largely contain unique mixture of mono and di terpenes. In the present work, we isolated essential oils from different plant parts including leaves, flowers and fruits which are using in our daily life and evaluated their Antitubercular activity and compared with antibacterial and anti-fungal activity.
The isolation of essential oils (As these are ethereal compounds) were carried out by solvent extraction method and evaluated for their antibacterial and antifungal activity by Cup-plate agar diffusion method, and the antitubercular activity was evaluated by MABA method.
Among the samples tested, the flower extracts of Mari gold (Orange and yellow), Tagetus patula, Chrysanthemum (White, Yellow, Maroon and Purple), Roses (Red and orange), the flower petals and stalks of Night jasmine (Nyctanthes arbor-tristis) and Jasmine (J. officinalis and J. multifluram) shown potent antitubercular and good antibacterial activity. All these flower extracts shown good anti-fungal activity except Jasmine species. Significant anti-fungal action was seen in the extracts of umbelliferous fruits like fennel, cumin, and caraway. Whereas aromatic plants (Mint and Sweet Marjoram) have shown both antibacterial and antifungal activity.
Essential oil of all the samples has shown potent antitubercular activity when comparing with standard drugs Rifampicin, Streptomycin etc, and it was noted that these are having selectivity towards mycobacterium when comparing with bacteria and fungi.

Wilson’s disease is a chronic, progressive disease with a genetically determined autosomal recessive mode of inheritance and multi-systemic condition, in which the copper is accumulated in the Kidneys, Eyes, Liver and especially in the basal ganglia in the central nervous system. In Wilson’s disease, the cirrhotic state of the liver is combined with degenerative changes in the lenticular nuclei of the brain, also known as hepato-lenticular degeneration. A 14-year-old male was admitted to the department of Paediatric with chief complaints of tremors of both upper limbs in the last 6 months, increased in intensity for 2 months. He was unable to button and unbutton the dress, handwriting was altered. He had splenomegaly, cirrhosis of the liver, bilateral Kayser-Fleischer rings, and gynecomastia. On investigation, his alkaline Phosphatase and albumin levels were increased and globulin, ceruloplasmin and serum copper levels were decreased. The patient was kept under copper chelators such as D-Penicillamine and zinc acetate. Gradually he showed improvement in clinical signs and Liver function tests. Prior recognition and awareness of Hepatic manifestations, KF rings, and involuntary movements of limbs will be useful for quick diagnosis and for preventing manifestations in siblings as this is an inherited metabolic disorder.